Organic chemistry: Alkenes and Alkynes Quiz 4
Organic chemistry : Alkanes quiz 3
Organic chemistry : Quiz2 – Alkanes
Organic chemistry: Alkanes
1 / 35
(36) The volume of gases produced from the thermal cracking reaction ………… are greatest
(a) C6H14(g) >>> 3C2H4(g) + H2(g).
(b)C8H18(g) >>> 2C3H8(g) + C2H2 (g)
(c) C10H22(g) >>> C8H18(g) + C2H4(g)
(d) C12H26(g) >>> C8H18(g) + 2 C2H4(g)
2 / 35
(34) The gas which is obtained from thermal catalytic cracking of octadecane C18H38 is ……….
(a) CO₂
(b) C18H36
(c) C36H74
(d) C9H18.
3 / 35
(33) Both of ………. are obtained from the thermal catalytic cracking of octane.
(a) hexane and ethane
(b) Butene and butane.
(c) heptane and methane
(d) propane and pentane
4 / 35
(32) Chlorine reacts with methane gas forming …………. in the presence of ultraviolet rays.
(a) chloromethane and hydrogen
(b) chloromethane and Hydrogen chloride
(c) dichloromethane and hydrogen
(d) dichloromethane and trichloromethane
5 / 35
31 ) Freons are used in air conditions and fridges, because they are ………..
(a) cheap.
(b) liquefied easily.
(c) non-poisonous and don't cause erosion.
(D) (a), (b) and (c).
6 / 35
(30) The molecular formula of chloroform is ………..
(a) CCl4
(b) CH2Cl₂
(c) CH4
(d) CHCI3.
7 / 35
(29) Alkanes react with halogens in the presence of ultraviolet rays by
(a) elimination.
(b) condensation.
(c) Substitution.
(d) reduction.
8 / 35
(28) The gas which burns in air forming two gases; one of them turns the clear limewater turbid and the other turns the anhydrous copper (II) sulphate into blue is …….
(a) Ethane.
(b) carbon monoxide
(c) hydrogen
(d) gasoline
9 / 35
(27) Alkanes which contain more than 17 carbon atoms are exist in state.
(a) Solid
(b) liquid
(c) vapour
(d) gaseous
10 / 35
(26) The boiling point of butane is less than that of ……….
(a) ethane.
(b) propane.
(c) methane.
(d) Hexane
11 / 35
(25) In hot countries, the fuel cylinders contain large amount of ……… gas.
(a) ethane
(b) propane
(c) Butane
(d) pentane
12 / 35
(24) In cold countries, the fuel cylinders contain high amount of
(a) methane
(b) ethane
(c) Propane.
(d) butane
13 / 35
(23) Which of the following compounds have the highest boiling point?.......
(a) Normal Hexane..
(b) Normal pentane.
(c) 2,2-dimethyl propane.
(d) 2-methyl butane
14 / 35
(22) Gasoline consists of compounds which contain …….. carbon atoms
(a) from 1:4
(b) from 4:5
(c) from 5:17.
(d) more than 17
15 / 35
(21) Soda lime is a mixture of ……..
(a) caustic soda and calcium carbonate
(b) caustic soda and Quick lime
(c) sodium carbonate and quick lime
(d) caustic soda and slaked lime
16 / 35
(20) The dry distillation of anhydrous sodium acetate with soda lime produces ……
(a) ethane.
(b) Methane.
(c) propane
(d) butane
17 / 35
(19) The boiling point of ……….. is less than that of the other three compounds
(a)C2H6 .
(b) CH3(CH₂)2CH3
(c)CH3(CH2)4CH3
(d)C8H18
18 / 35
(18) With increasing the molecular mass in alkanes, the property ………. doesn't increase
(a) boiling point
(b) Ability to burn
(c) melting point
(d) viscosity
19 / 35
(17) Complete burning of 1 mole of ……….. produces 3 mole of CO2, and 4 moles of H2O
(a) C3H8.
(b) C3H4
(c) C2H4
(d) C2H2
20 / 35
(16) 1 L of gas …… reacts with 5 L of O2 , at STP
(a)CH4
(b) C2H6
(c) C3H8.
(d)C4H10
21 / 35
(15) Burning of 20 cm3 of gas …… in an excess of O2
At STP produces 60 cm3 of CO2
- a) C3H6.
(b) C4H10
(c) C6H12
(d) C6H14
22 / 35
(14) The gas which causes the decay of the ozone layer is
(a) CH3CH2CH3
(b) CH3CHCI2
(C) CH3OCH3
(D) CF2Cl2
23 / 35
(13) 2-methyl pentane is considered the isomer of the compound ………….
(a) 2-methyl butane.
(b) (2,2-dimethyl Butane
(c) 2,2-dimethyl pentane
(d) 2,2-dimethyl propane
24 / 35
(12) The number of ethane molecules which are present in 15 g of it equals to……….. molecule (c=12,H=1)
(a) 0.5
(b.) 3.01 x 1023
(c) 6.02 x 1023
(4) 2.04 x 1023
25 / 35
(11)2,2-dimethyl pentane contains ……. methylene group (-CH2)
(a)1
(b.)2
(c)3
(d)4
26 / 35
(10) On removing hydrogen atom from propane,
(a)-CH3
(b)-C3H7.
(c)-C2H5
(d)C4H9
27 / 35
(9) The general formula of alkyl group is …….
(a) CnH2n
(b) CnH2n+2
(c) CnH2n+1.
(d)Cn H2n-1
28 / 35
(8) In the homologous series, each compound exceeds the previous by
(a)-CH3
(b.)-CH₂
(c)-C2H5
(d)-C6H5
29 / 35
( 7) The alkane which contains 4 carbon atoms has …. sigma bonds.
(a) 11
(b) 12
(d) 14
(C) 13
30 / 35
(6) The alkane consists of 14 atoms which contains ……… carbon atoms.
(a) 4.
(b) 7
(c) 8
(d) 10
31 / 35
(5) The number of carbon atoms in the alkane which contains 10 hydrogen atoms is ………. atoms.
(a) 4.
(b) 5
(c) 8
(d)10
32 / 35
(4) The number of hydrogen atoms in the alkane which contains 14 carbon atoms is -----
(a) 14
(b) 26
(c) 28
(d) 30.
33 / 35
(3) The number of hydrogen atoms in the alkane which contains 4 carbon atoms is atoms.
(a) 5
(b) 7
(c) 8
(D) 10
34 / 35
(2) The molecular formula of alkane which contains five carbon atoms is ….
(a) C5H8
(b) C5H9
(c) C5H12.
(d) C5H10
35 / 35
(1) The general formula of alkanes is ….
(a) CnH2n+1 (b) CnH2n+2.
(c) CnH2n (d) CnH2n-2
Your score is
The average score is 73%
Quiz2:chapter3: chemical equilibrium
Quiz2:chapter3: chemical equilibrium
Quiz2:chapter3: chemical equilibrium
1 / 30
(36) The equilibrium of the reaction:
N2(g) + O2(g) ↔ 2NO(g) - energy
is not affected by ---------------
(a) increasing the temperature.
(b) increasing the concentration of nitrogen gas
(c.) decreasing the pressure.
(d) removing nitric oxide from the reaction
2 / 30
(35) In the reaction:
2SO2(g)+O2(g) ↔ 2SO3(g) + energy
the formation of sulphur trioxide increases as …………………
(a) the temperature decreases.
(b) the pressure increases.
(d.) (a), (b) and (c).
(c) SO3 is removed from the reaction.
3 / 30
(34) Enzymes act as -----.agents in biological and industrial processes.
(a) oxidizing
(b.) catalytic
(c) drying
(d) antiseptic
4 / 30
(33) The catalysts are considered
(a) metallic elements.
(b) basic oxides.
(c) metallic compounds.
(d.) (a), (b) and (c).
5 / 30
(32) All the following catalyst properties may be affected during the chemical reaction.except
(a) its appearance.
(b) its surface area.
(c) its physical properties.
(d.) its chemical structure.
6 / 30
(31) The catalyst accelerates the chemical reaction because
(a) it increases the distances between the reactants.
(b.) it decreases the activation energy of the reactants.
(c) it affects the equilibrium point.
(d) (a). (b) and (c).
7 / 30
(38) Increasing the pressure in the following equilibrium reaction:
N2(g) + O2(g) ↔ 2NO(g) – energy
causes the reaction to shift in the direction which -----------
(a) decreases the absorbed heat.
(b) increases the concentration of nitrogen gas.
(c) decreases the number of produced moles.
(d.) no correct answer.
8 / 30
(39) The rate of the forward reaction increases by increasing the temperature and decreasing the pressure in the reaction
(a) H2(g) + I2(g) ↔ 2HI(g) ΔH = +ve
(b)NO(g) ↔ ½ O2(g) + ½ N2(g) ΔH = -ve
(c) N2H4(g) ↔ N2(g) +2H2(g) ΔH = -ve
(d.)2NH3(g) ↔ N2(g) +3H3(g) ΔH = +ve
9 / 30
(40) The gelatinous layer in photographic films contains ------
(a) sodium chloride.
(c) silver nitrate.
(b.) silver bromide.
(d) potassium iodide.
10 / 30
(51) Consider the following equilibrium system:
2O2(g) ↔ 3O2(g) Kc=36
What is the concentration of O3(g) when the equilibrium concentration
Of is 5.8 x 10-2 mol/L ? -----------
(a.) 2.32 x 10-3 mol/L
(b) 4.54 x 10-3 mol/L
(c) 3.87 x 10-3 mol/L.
(d) 8.7 x 10-3 mol/L.
11 / 30
(50) Consider the following equilibrium system:
N2(g) + O(g) + heat ↔ 2NO(g)
The amount of NO can be increased by
(a) decreasing the amount of O2
(b.)increasing the temperature of the reaction.
(c) increasing the pressure.
(d) decreasing the amount of N2
12 / 30
(49) Equal volumes of 1 mol/l solutions of W and X are mixture.
The reaction below rapidly reaches equilibrium?
W(aq) + X(aq) ↔Y(aq) +Z(aq)
At equilibrium, the concentration of Y(aq) is found to be 4 mol/L. What is the value of
Kc for the above reaction?
(a) 0.25
(b) 0.44
(c)4.0
(d.)16
13 / 30
(47) Consider the following system of equilibrium:
H2O(V)+CO(g) ↔ CO2+H2(g)
The position of equilibrium shifts to the right as the result of the addition of some extra
H2O(V) How will this shift affect the concentrations of the other gases
(a) [CO] increases, [CO2] decreases and [H2] decreases.
(b) [CO] increases, [CO2] increases and [H2] decreases.
(c) [CO] decreases. [CO2] decreases and [H2] increases.
(d.) [CO] decreases. [CO2] increases and [H2] increases.
14 / 30
(46) Consider the following equilibrium system:
CO(g)+H2O(v) CO2(g) +H2(g)
Which of the following actions would cause the concentration of H2(g) to decrease?……
(a) Adding CO(g)
(b) Adding H2O(v)
(c) Removing CO2(g)
(d.) Removing H2O(v)
15 / 30
(45) Consider the following equilibrium system:
N2H4(g)+2O2(g) ↔2NO(g) +2H2O(g)
Which of the following action can cause the position of equilibrium to shift to the right?
(a.) Adding N2H4(g)
(b) Adding H2O(g)
(c) Removing N2H4(g)
(d) Removing O2(g)
16 / 30
(44) Consider the following reaction:
CO2(g) + H2(g) ↔ CO(g) +H2O(v)
1 mole of CO2 and 2 moles of H2(g) are placed in a 2L container. At equilibrium the concentration of CO(g) is 0.28 mol/L.
What is the equilibrium concentration of CO2(g) and the equilibrium constant, Kc for the reaction?
(a.) 0.22 mol/L, and 0.495
(b) 360 mol/L and 0.0081
(c) 0.44 mol/L and 2.02
(d) 0.72 mol/L. and 123
17 / 30
(43) Which of the following is incorrect for a system at equilibrium?
(a) The system has a constant mass.
(b) The system acts to oppose disturbances.
(c) The forward and backward reactions proceed at the same rate.
(d.) The reactant and product concentrations vary with time.
18 / 30
(42) Nitrogen dioxide decomposes on heating according to the following equation
2NO2(g) ↔ 2NO(g)+O2(g)
When 6.80 moles of NO2(g) were put into a 1.00L container and heated, the equilibrium mixture contained 1.2 moles of O2(g) What is the equilibrium constar
Kc for the reaction?...........
(a.) 0.357
(b) 0.655
(c) 1.53
(d) 2.80
19 / 30
(41) Phosphorus reacts with chlorine according to the following equation:
P4(s)+6Cl2(g) ↔ 4PCl3(g)
What is the equilibrium constant, Kc, for the reaction?
(a)4[PCl3] / [P4][Cl2]
(b ) 4[PCl3] / 6[Cl2]
(c)[PCl3]4 / [P4][Cl2]6
(d.) 4[PCl3]4 / [Cl2]6
20 / 30
(52) An equal number of moles of steam and chlorine are placed in a closed container
at 375 K. The following reaction occurs:
2H2O(g)+2Cl2(g) ↔ 4HCl(g) +O2(g) Kc=5x 10-4 at 375°K
Which of the following relates [Cl2] and [HCI) at equilibrium?
(a) [Cl2] <2 [HCI]
(b.) [Cl2]2>[HCI]4
(c) [Cl2]=2[HCI]
(d) [Cl2]²= [HCI]4
21 / 30
(53) 2SO2(g)+O2(g) ↔ 2SO3(g) Kc= 4.5
In an experiment, a mixture of 4 moles of sulphur dioxide and 1.5 moles of oxygen is allowed to reach equilibrium.
The moles of SO3 are -----------------
(a) 5.5 moles.
(b) 4 moles.
(c) 3 moles.
(d.) less than 3 moles.
22 / 30
(54) Consider the following equilibrium system in a closed vessel reaction:
CH3CHO(g) ↔ CH4 +CO2(g) ΔH>0
What would happen if some CH4(g) is added to the system? -------------
(a) The amounts of all substanses increases, relative to their previous equilibrium amounts.
(b) The value of Kc increases.
(c) The amounts of CH3CHO(g) and CO(g) both increase, relative to their previous
equilibrium amounts.
(d.) The amount of CH3CHO(g) increases, relative to the previous equilibrium amounts.
23 / 30
(61) For which of the following equilibrium system will the amounts of reactants increase
with an increase in the container volume ?
(a) C(g) +CO2(g) ↔ 2CO(g)
(b) N2(g) + 3H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g)
(c) 2NO(g) + O2(g) ↔ 2NO2(g)
(d.) Both (b) and (c).
24 / 30
(60) Consider the following equilibrium system:
PCl3(g)+O2(g) ↔ PCl5(g)
Which of the following statements is/are correct when the volume of the system is decreased?
(a.) The position of equilibrium shifts to the right.
(b) The rate of the backward reaction increases.
(c) The value of Kc increases.
(d) Both (a) and (b).
25 / 30
(59) Consider the following equilibrium system:
2SO2(g) + O2(g)↔ 2SO3(g) K=1.2×104
Some of SO2(g) is added to the equilibrium system.
Which of the following statements are correct?
(a.) The position of equilibrium shifts to the right.
(b) The rate of the forward reaction increases.
(c) The value of Kc increases,
(d) Both (a) and (b).
26 / 30
(58) In the equilibrium system: in presence of ZnO /Cr2O3
CO(g) + 2H2(g) ↔ CH3OH(g)
Which of the following combinations describes the effect of removing the catalyst (ZnO/Cr2O3) from the above system?
(a) Equilibrium yield decreases and reaction rate decreases.
(b.) Equilibrium yield unchanged and reaction rate decreases.
(c) Equilibrium yield and reaction rate are unchanged.
(d) Equilibrium yield decreases and reaction rate unchanged.
27 / 30
(57) Methanol is manufactured by the reaction of carbon monoxide with hydrogen in the presence of a ZnO/Cr2O7 catalyst:
CO(g) +2H2(g) ↔ CH3OH(g)
Which of the following combinations describes the effect of increasing the pressure
of the system?
(a) Equilibrium yield decreases and reaction rate increases.
(b) Equilibrium yield decreases and reaction rate decreases.
(c.) Equilibrium yield increases and reaction rate increases.
(d) Equilibrium yield increases and reaction rate decreases.
28 / 30
(56) The system below reaches equilibrium in a closed reaction vessel
4HCl(aq) + MnO2(s) ↔ 2Cl2(g)+2H2O(l)+ Mn2+(aq) +2Cl-(aq) ΔH<0
Which of the following actions will increase the mass of Cl2(g) in the equilibrium mixture?
(a) Adding some MnO2
(b) Increasing the temperature.
(c) Decreasing the volume of the reaction vessel.
(d.) Adding something that precipitates the Mn2+ ions.
29 / 30
(55)* From the following equilibrium constants:
H2S(aq) ↔ H+(aq) + HS-(aq) Kc=9.5
HS-(aq) ↔ H+(aq) + S2- Kc=1x10-19
What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction?
S2-(aq) +2H+(aq)↔ H2S(aq)
(a) 9.5 x 10-27
(b) 9.75 x 10-14
(c) 9.5 x 1011
(d.) 1.05 x 1026
30 / 30
(64) Which of the following statements about enzymes are correct?
(a) Enzymes are proteins.
(b) Enzymes increase the rate of biochemical reactions.
(c) Enzymes increase the equilibrium constant of biochemical reactions.
(d.) Both (a) and (b).
Your score is
The average score is 18%
Quiz 1: chapter3:Chemical equilibrium
chapter3:chemical Equilibrium Quiz1
1 / 30
(1) Equilibrium system is described as dynamic because
2 / 30
(2) The reaction of hydrochloric acid with magnesium is a complete reaction because
3 / 30
(3) --------- is a one of the instantaneous reactions.
4 / 30
(4)---------- is a one of the comparatively slow reactions.
5 / 30
(5) The solution of the reaction of acetic acid with ethyl alcohol turns litmus paper red because
6 / 30

7 / 30
(7) The opposite figure represents -----
8 / 30
20) The Kc of the reaction:
SnO2+2CO(g) ↔ Sn(s)+2CO2(g)
Is -------------------------
(a) Kc= [CO₂] / [CO]
(b.) Kc= [CO2]2 / [CO]2
(c) Kc= [Sn].[CO₂]² / [SnO2][CO2]2
(d) Kc= [Sn] [CO2]² / [CO]2
9 / 30
(19) The rate of a chemical reaction:
Zn(s) + 2HCl(g) ↔ ZnCl2(aq) +H2(g)
is measured by changing in-------------------
10 / 30
(18) When temperature of the following reaction:
H₂+I2 ↔ 2HI
is raised, the increasing in K1, is less than that of K,2. So, the equilibrium constant Kc ------------
11 / 30
(17) From the Kc value of the reaction:
2SO3(g) ↔ 2SO2(g)+O2 , Kc=1.2x10-4
we can conclude that -----------
12 / 30
(16) From the Kc value for the reaction:
H2(g) + Cl2(g) ↔ 2HCl(g) .Kc=4.4 × 1032
we can conclude that ------
13 / 30
(11) ------- established a law expressing the relationship between the rate of the chemical reaction and concentration of the reactants.
14 / 30
(12) The chemical reaction is in equilibrium when --------
15 / 30
(13) In the following equilibrium reaction:
FeCl3(aq) +3NH SCN(aq) ↔ Fe(SCN)3(aq) + 3NH4Cl(aq)
The rate of reversible reaction is expressed by --------
16 / 30
(14) K1/K2 for an equilibrium reaction is known as K
17 / 30
(15) When the value of equilibrium constant is high, it means that ---------
18 / 30
(8) Each of the following affects the chemical equilibrium except the --------- if the volumes of reactants and products are different.
19 / 30
(9) The reaction:
N2(g) + 3H2(g) = 2NH3(g) (N=14, H=1]
reaches the equilibrium state when are present in a closed flask. (at S.T.P)
20 / 30
(10) In the reaction: Vegetable oil +H2(g) in presence of Ni /Δ → Margarine (artificial fat)
the nickel used is preferred to be in the form of ......
21 / 30
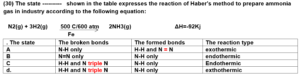
22 / 30
(29) On increasing the reactants concentrations of a reaction under equilibrium, a shift in the direction of --------
takes place.
23 / 30
(21) The concentration of reactants equals the concentration of products at the equilibrium reaction reaction --------
a)Na2O4(g) ↔ 2NO2(g) Kc=0.71
b)H+(aq) +OH-(aq) ↔ H2O(l) Kc= 1x 10 14
c)CO2(g) +H2(g) ↔ CO(g)+ H2O(v) Kc=0.297
d.)SnO2(s) +2H2(g) ↔ Sn(s)+2H2O(v) Kc=1
24 / 30
(28) On increasing the pressure on a gaseous reaction under equilibrium, a shift in the direction of -------------takes place.
25 / 30
(27) by increasing the reaction temperature 10°C
26 / 30
(26) The Kc value of the reaction changes when -----
27 / 30
(25) The concentration of gases is preferable to expressed by
28 / 30
(24) The orange colour turns yellow on adding -------- to the follwing reaction:
2CrO42- (aq) + 2H3O+(aq) ↔ Cr2O72- + 3H2O(l)
Yellow orange
(a) KNO3 (b.) NaOH
(c)NH4NO3 (d)CH3COOH
29 / 30
(23) The Kc value equals Kp for the reaction
(a) PCl5(g) ↔ PCl3(g) +Cl2(g)
(b)2SO2(g)+O2(g) ↔ 2SO3(g)
(c.) H2(g) + I2(g) ↔ 2HI(g)
(d) N2(g) +3H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g)
30 / 30
(22) Which of the following changes increases the kinetic energy of the reactant molecules ? -------------------
(a) The decreasing of concentration
(b.) The increasing of temperature.
(c) The increasing of surface area.
(d) The increasing of concentration.
Your score is
The average score is 34%
Quiz1:oraganic compounds and classification of Hydrocarbons
chapter5: Organic chemistry
organic compounds and classification of Hydrocarbons
1 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(44) On burning an organic substance with copper oxide, ----------- are produced.
2 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(31) Most of organic compounds soluble in ------
3 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(10) The bonds in organic compounds are .......bonds.
4 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(32) The boiling and melting points of organic compounds are
5 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(35) The formula that shows the number and the type of atoms only in the molecule formula.
6 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(44) We can detect the presence of water by using ---------------
7 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(38) The compound with the structural formula: Follows a group of the compounds
whose general formula is
(a) C2nH5nOn (c) CnH2n+2O2
(b)CnH2nO2 (d) CnH2n-2O2
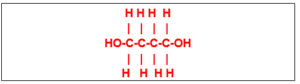
8 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(46) The molecular formula of aromatic benzene is ----------
9 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(36) The phenomenon that many organic compounds have the same molecular formula is called............
10 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(42) Propyne (C2H4) is an example of ---------------
11 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(40) Any combination of the following hydrocarbons represents the isomer to the another one ?
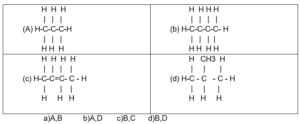
12 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(41) The organic compounds with formula C2H4, is ------------ compound
13 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(45) Benzene and naphthalene are examples of hydrocarbons.
14 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(33) Reactions between organic compounds are slow because they take place between..........
15 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(40) The hydrocarbons with the molecular formula CnH2n+2 are
16 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
30)The carbon atoms can combine with each other by............bonds.
17 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(43) The molecular formula C6H12 is a formula of -------------
18 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(39) The corresponding two compounds are similar in-------- and differ in ------------
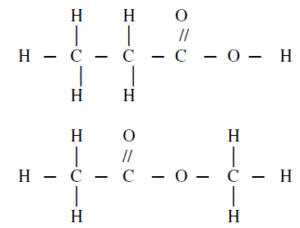
19 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(37) All organic compounds contain------ in their structure.
20 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(47) The molecular formula of naphthalene is....
21 / 50
Category: chapter5:organic chemistery
(2) The compounds which are extracted from mineral sources in the Earth.
22 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(8) The formula which indicates the kind and number of the atoms of each element in
the compound.
23 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(1) The compounds which have been thought that they are extracted from plants and animals only.
24 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(4) The first organic compound that was prepared in Lab. not in the living cells
25 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(15) The unsaturated open chain aliphatic hydrocarbons, which are characterized by the presence of a double bond at least in the carbon chain.
26 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
24)The scientist who classified the compounds into organic and inorganic compounds
27 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(19) Unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons, their general molecular formula are : CnH2n
28 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(5) The organic compound that was obtained on heating aqueous solutions of ammonium chloride and silver cyanate.
29 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements


30 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(11) The substance which added to the organic compound to detect the presence of carbon and hydrogen.
31 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
25) The scientist who destroyed the vital force theory is.....
32 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(21) The organic compounds in which all the corners of the ring have carbon atoms only
33 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(3) A theory which considered that organic compounds are formed in the cells of living organisms only.
34 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(28) The organic chemistry focused on the study of carbon element with exception of
35 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
23)Classify the following compounds into : (alkanes – alkenes - alkynes):
(1) C3H8 (2) C7H₁₂ (3) C6H12 (4) C4H10 (5) C40H82 (6) C5H12
36 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(14) The saturated cyclic aliphatic hydrocarbons.
37 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(6) The basic element in all the organic compounds.
38 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(9) The formula which indicates the type of linkage between the atoms by the covalent bonds.
39 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
26) The carbon atoms of thiophene are bonded with sulphur in the form of compound.
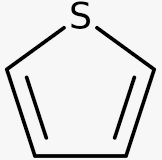
40 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(26) The organic compound which is obtained on heating ammonium cyanate is ------
41 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(27) All the following compounds are organic compounds except
42 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(16) The unsaturated open chain aliphatic hydrocarbons, which are characterized by the presence of a triple bond at least in the carbon chain.
43 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(7) The branch of Chemistry that focused on the study of carbon element with exception of carbon oxides, carbonate and cyanide salts.
44 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(10) It is a phenomenon that many organic compounds have the same molecular formula but differ in structural formula.
45 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
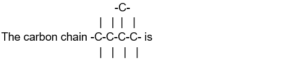
46 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(12) The organic compounds which consist of carbon and hydrogen only.
47 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(22) The organic compounds in which the corners of the ring have carbon atoms and other atoms of different elements.
48 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(13) The saturated open chain aliphatic hydrocarbons.
49 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(18) Cyclic hydrocarbons, their general molecular formula are CnH2n+2
50 / 50
Category: chapter1 Transition Elements
(20) Unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons, their general molecular formula are: CnH2n-2
Your score is
The average score is 32%
الاختبار (1) عناصر السلسلة الانتقالية الأولى
Quiz7:The properties of the First transition series
Quiz8:chapter1:The electronic configuration of The Transition Elements
Quiz4:chapter one Transition elements
Quiz1:chapter2 chemical analysis
Quiz1:chapter2 chemical analysis (dil. HCl )group
chemical analysis , the types of chemical analysis ,qualitative
analysis and
analysis quantitative
1 / 31
chemical analysis is useful in etraction iron from its ores because it ….
2 / 31
Analysis of inorganic compounds included detection of ……
3 / 31
To identify chemical formula of a compound we should identify ……
4 / 31
To identify a substance by measuring its molar mass or melting point it should be …
5 / 31
The most stable acid is ….
6 / 31
7)The most stable acid is ….
7 / 31
Dil. HCl can detect all the following except ….
8 / 31
Anion (A) from dil. HCl groups ……
9 / 31
Acid form which nitrate ion is derived from is ….
10 / 31
Dil. HCl is used to detect CO32- because …
11 / 31
If A=K2CO3 , B=CaCO3 and C=(NH4)2CO3
12 / 31
Ca(HCO3)2 and Al(HCO3)3 are two salts :
13 / 31
Which of the following pairs of ions forms ppt. when mixed with a dilute aqueous medium ?
14 / 31
All carbonate of Na+ ,Mg2+, Ca2+ are soluble in ….
15 / 31
All bicarbonate of Na+ ,Mg2+, Ca2+ are soluble in ….
16 / 31
which of the following may give a white ppt.
17 / 31
By adding dil. HCl to salts of unstable acids it can replace them in the form of …..
18 / 31
All of thes unstable acids replaced by dil. HCl then decoplosed except …
19 / 31
By adding dil. HCl to ……… salt it gives a bad smell gas
20 / 31
By adding dil. HCl to ……… salt it gives gas turbid lime water
21 / 31
By adding dil. HCl to ……… salt it gives an irritating smell gas
22 / 31
By adding dil. HCl to a solid ……… salt it gives colorless gas turns into reddish brown gas at the mouth of the tube
23 / 31
By adding MgSO4 to ……… salts solutions it gives white ppt on cold
24 / 31
By adding MgSO4 to ……… salts solutions it gives white ppt after heating
25 / 31
By adding AgNO3 to ……… salt solutions it gives black ppt directly
26 / 31
By adding AgNO3 to ……… salt solutions it gives balck ppt after heating
27 / 31
By adding I2 solution to ……… salt solutions it removes the brown color of I2
28 / 31
By adding acidified KmnO4 solution to ……… salt solutions it removes the brown color of I2
29 / 31
By adding AgNO3 to ……… salt solutions it gives white ppt. that turns into balck ppt after heating
30 / 31
By adding dil. HCl to ……… solid salt it gives irritating smell gas and a yellow ppt of an element
31 / 31
By adding dil. HCl to ……… solid salt it gives irritating smell gas ,and changes a pape wet with acidified potsium dicromate from orange to green yellow ppt of an element
Your score is
The average score is 31%