Modern periodic table: Arrangement of Elements ,Blocks
Modern periodic table: Arrangement of Elements ,Blocks
Explore the organization of elements in the modern periodic table, understand the significance of atomic number, and discover the key groups and blocks. Learn about alkali metals, noble gases, transition metals, and more.
The modern Periodic table
The modern periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. It was developed based on the principles of Dmitri Mendeleev and Julius Lothar Meyer in the late 19th century and has since undergone several revisions and improvements.
The current version of the periodic table as of my knowledge cutoff date in January 2022 is based on the long-form periodic table.
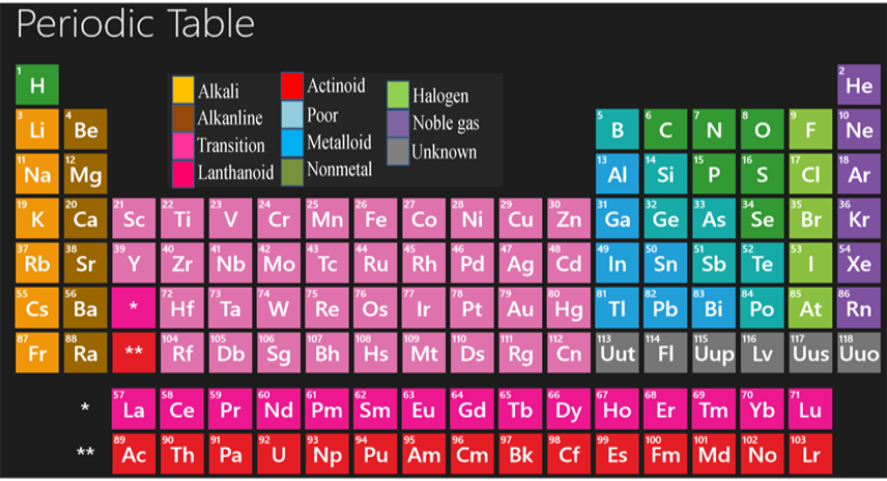
Here are some key features of the modern periodic table:
-It consist of 118 elements distributed in 7 periods (horizontal raws) and 18 groups (vertical columns).
The elements are arranged ascending according to :
1-Their atomic numbers(number of protons):
The atomic number of each element exceeds the element which precedes it in the same period by one
2-The sequences of filling their atomic energy sublevels with electrons according to the Aufbau (building up )principle where each element has one electron more than the element which precedes it.
Each period begins by filling a new principle energy level with one electron the filling the atomic energy sublevels lying in the same period successively until the last element in the period which is noble gas that has completely filled energy level
The following keywords of the periodic table
Rows (Periods):
- The periodic table is organized into rows, known as periods, which represent the number of electron shells or energy levels in an atom.
- There are seven periods in the modern periodic table.
Columns (Groups):
- The table is divided into columns, known as groups or families, based on similar chemical properties.
- Elements within the same group tend to have similar electron configurations and exhibit similar chemical
- There are 18 groups in the modern periodic table.
Atomic Number: Elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number (the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom).
This is the fundamental organizing principle of the periodic table.
Chemical Symbol: Each element is represented by its chemical symbol, typically one or two letters derived from the element’s name.
For example, H for hydrogen, O for oxygen, and Fe for iron.
Blocks: The periodic table is often divided into four main blocks:
s-block,
p-block,
d-block, and
f-block,
based on the subshells being filled with electrons.
These blocks represent different regions of the table.

The arrangement of elements in modern periodic table depends on:
The arrangement of elements in the modern periodic table depends on the following key principles:
Atomic Number:
The most fundamental organizing principle of the modern periodic table is the atomic number of each element.
The atomic number represents the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom and is a unique identifier for each element. Elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic number from left to right across each row (period) of the table.
Periodic Law:
The periodic table is based on the periodic law, which states that the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. In other words, elements with similar chemical properties recur at regular intervals when arranged by atomic number.
Rows (Periods):
- The periodic table is organized into rows known as periods.
- Each period represents a different energy level or electron shell in an atom.
- There are seven periods in the modern periodic table, with the first period containing two elements, the second period containing eight elements, and so on.
Columns (Groups or Families):
- The table is divided into columns known as groups or families.
- Elements within the same group share similar chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons and similar electron configurations.
- There are 18 groups in the modern periodic table, often labeled with a number or a number and a letter (e.g., Group 1, Group 2, Group 18).
Electron Configuration:
- The arrangement of elements in the periodic table reflects their electron configurations, which describe the distribution of electrons in the atomic orbitals.
- Elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons, which influences their similar chemical reactivity.
Block Classification:
- The periodic table is divided into blocks based on the electron subshells that are being filled with electrons.
- The main blocks are the s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block, each representing a specific set of electron orbitals.
- Elements in these blocks have distinct properties related to their electron configurations.
The elements blocks of the modern periodic table:
- The modern periodic table is divided into several blocks, each of which represents a specific set of electron orbitals being filled with electrons. These blocks are typically labeled with letters to indicate their position in the periodic table and their electron configuration.
- The main blocks include the s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block, while the g-block is a hypothetical extension beyond the known elements.
Here’s an overview of the elements blocks in the modern periodic table:
S-Block:
-Elements in the s-block are characterized by their outermost electrons filling s-orbitals.
– They lie in the left-side of the table.
-The s-block includes two groups:
- Group 1A: Alkali Metals (e.g., lithium, sodium, potassium) whose electronic configuration ends with ns1.

- Group 2A: Alkaline Earth Metals (e.g., beryllium, magnesium, calcium) whose electronic configuration ends with ns2.

N is number of energy level and and the number of period
P-Block:
- Elements in the p-block have their outermost electrons filling p-orbitals except Helium.
- They are in the right side of the table.
- The p-block includes six groups characterized by symbol “A “ except Zero group ( from Group 13 to Group 18) and contains nonmetals, metalloids, and some metals.
- Notable elements in the p-block include carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and the halogens (Group 17).
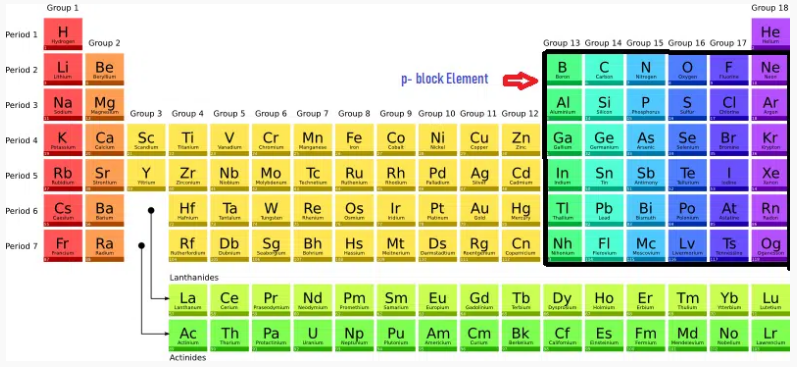
General electronic configuration of s,p,d,f block element

D-Block:
- Elements in the d-block have their outermost electrons filling d-orbitals.
- Consist of 10 vertical columns and 8 groups
- Characterized by the symbol “B” except eighth group(VIII) which consists of “3” vertical columns.
- These elements are known as transition metals and exhibit a wide range of oxidation states.
- The d-block spans from Group 3B to Group 2B and includes elements like iron, copper, and zinc.
- They are in the middle of the table
- D-block elements are classified according the number of the outermost energy level and the period number into three series

These four series are:
First Transition Series:
- This series includes the transition elements from Scandium (Sc) to Zinc (Zn).
- The first transition series is found in the fourth period of the periodic table, starting from the 3d subshell.
- The electron configuration for these elements begins with 3d1 (Scandium) and progresses through 3d10 (Zinc).
- These elements exhibit typical transition metal properties, such as variable oxidation states, formation of colorful compounds, and the ability to act as catalysts.

Second Transition Series:
- This series includes the elements Yttrium (Y) and Cadmium (Cd).
- Yttrium is considered the first element in the second transition series, and it is located just below Scandium in the periodic table.
- Yttrium and the elements in the first transition series share many similar properties.

Third Transition Series:
- The third transition series consists of the elements Lanthanum (La) to Mercury (Hg).
- These elements are found in the sixth period of the periodic table, and their electron configuration starts with the 4f subshell.
- While the lanthanides are often considered part of this series, they are sometimes treated separately because of their distinct electron configurations and properties.

Fourth Transition Series:
- The fourth transition series includes the elements Actinium (Ac) to Copernicium (Cn).
- This series begins with the 5f subshell and continues into the 6d
- These elements are found in the seventh period of the periodic table.
- Most of the elements in this series are synthetic and are not naturally occurring.
They share many properties with the first and second transition series elements.
It’s important to note that the transition elements are characterized by their partially filled d-orbitals, which gives rise to their unique properties, including variable oxidation states, magnetic properties, and the ability to form complex ions and compounds.
They are essential in various chemical reactions, industrial processes, and technological applications due to their versatile chemistry.
f-block elements
- The f-block is found at the bottom of the periodic table and includes two series of elements:
- The f-block elements, also known as inner transition metals, are a group of elements located at the bottom two rows of the periodic table.
- These elements are divided into two series:
the lanthanides and the actinides.
- The f-block elements are unique because of their electron configurations, which involve the filling of f-orbitals.
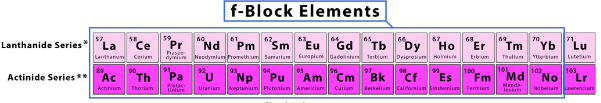
Lanthanides:
- The lanthanide series consists of 15 elements, starting with Lanthanum (La) and ending with Lutetium (Lu).
- These elements are part of the sixth period of the periodic table, and their electron configurations involve filling the 4f- orbitals.
- They were named –inaccuracy- by rare earths because Lanthanides are known for their similar chemical properties, which makes them difficult to separate from one another as the outermost energy level for all of them is 6S2.
- However that name is not accurate as recently their oxides can be separated by ionic exchange.
.The lanthanides include the following elements (atomic numbers 57-71 and 89-103): La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, and Lu.
Actinides:
- The actinide series consists of 15 elements, starting with Actinium (Ac) and ending with Lawrencium (Lr).
- These elements are part of the seventh period of the periodic table and have electron configurations that involve filling the 5f orbitals.
- Unlike the lanthanides, many actinides are radioactive, and some are artificially synthesized.
- The actinides include well-known elements like Uranium and Thorium, which are important in nuclear energy production.
- The actinides include the following elements (atomic numbers 89-103 and 104-118): Ac, Th, Pa, U, Np, Pu, Am, Cm, Bk, Cf, Es, Fm, Md, No, Lr, and elements beyond Lr are still under investigation.
- All of them are radioactive and their nuclei are unstable.
Both the lanthanides and the actinides share certain common characteristics, such as similar chemical behavior and the presence of f -orbitals in their electron configurations.
These elements have unique properties that stem from their electron structures and are crucial in various scientific, industrial, and nuclear applications.
s-block elements:
The s-block elements are a group of elements in the modern periodic table where the outermost electrons are filling the s-orbitals. These elements are found in the first two groups of the periodic table, specifically in Group 1 (the alkali metals) and Group 2 (the alkaline earth metals). The s-block elements are known for their distinctive chemical properties, which are primarily related to their valence electron configurations.
Here is an overview of the s-block elements:
Group 1: Alkali Metals
- Alkali metals are found in Group 1A of the periodic table.
- They include lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K), rubidium (Rb), cesium (Cs), and francium (Fr).
- Alkali metals are highly reactive and tend to form +1 cations by losing their single valence electron to achieve a stable electron configuration.
- They are soft, have low melting and boiling points, and are known for their strong alkali properties when combined with water.

Group 2: Alkaline Earth Metals
Alkaline earth metals are found in Group 2 of the periodic table.
They include beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).
Alkaline earth metals are also reactive, though less so than alkali metals, and tend to form +2 cations by losing their two valence electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration.
They are harder and denser than alkali metals and have higher melting and boiling points.

S-block elements are known for their strong tendency to lose their valence electrons, resulting in the formation of cations with a noble gas electron configuration. This behavior makes them highly reactive and useful in various chemical and industrial applications. Alkali metals, in particular, are known for their use in batteries, while alkaline earth metals find applications in the production of strong structural materials and in the preparation of certain chemical compounds.
Here is an overview of the p-block elements:
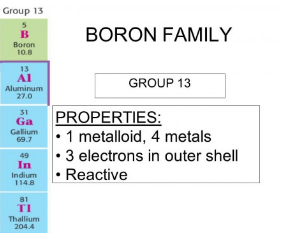
Group 13: Boron Group
- Group 13 includes boron (B), aluminum (Al), gallium (Ga), indium (In), and thallium (Tl).
- These elements have three valence electrons and typically form +3 cations.
- Boron is a nonmetal, while the others are metals or metalloids.
Group 14: Carbon Group
- Group 14 includes carbon (C), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), tin (Sn), and lead (Pb).
- These elements have four valence electrons.
- Carbon is a nonmetal, while silicon and germanium are metalloids, and tin and lead are metals.

Group 15: Nitrogen Group
- Group 15 includes nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), and bismuth (Bi).
- These elements have five valence electrons.
- Nitrogen is a nonmetal, while phosphorus is a nonmetal or metalloid, and arsenic, antimony, and bismuth are metals.
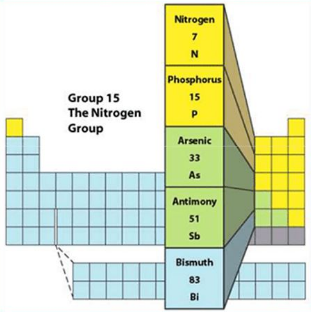
Group 16: Oxygen Group (Chalcogens)
- Group 16 includes oxygen (O), sulfur (S), selenium (Se), tellurium (Te), and polonium (Po).
- These elements have six valence electrons.
- Oxygen and sulfur are nonmetals, while selenium and tellurium are metalloids, and polonium is a metal.

Group 17: Halogens
- Group 17 includes fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At).
- These elements have seven valence electrons.
- Halogens are highly reactive nonmetals that readily form -1 anions when combined with other elements.

Group 18: Noble Gases
- Group 18 includes helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and radon (Rn).
- These elements have full electron shells and are chemically inert.
- They are known as noble gases.
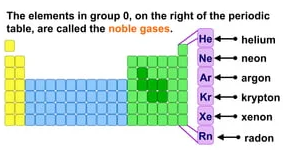
P-block elements exhibit a diverse range of properties due to variations in their electron configurations and bonding tendencies. They include nonmetals, metalloids, and metals, as well as highly reactive halogens and the chemically inert noble gases. The p-block elements play essential roles in a wide range of chemical compounds, and their chemical reactivity depends on their valence electron configurations.
Quiz with answers about this lesson
Here’s a quiz about the arrangement of elements in the modern periodic table, along with the answers:
Quiz Questions:
1-What is the fundamental organizing principle of the modern periodic table?
2-How many periods are there in the modern periodic table?
3-What are the columns in the periodic table known as?
4-What is the significance of the atomic number in the arrangement of elements?
5-Which group in the periodic table contains the alkali metals?
6-Which group in the periodic table contains the noble gases?
7-Elements in the d-block are commonly referred to as what?
8-What is the key property that differentiates elements in the f-block from other elements?
9-Which group in the periodic table contains the halogens?
10-What is the name for the second series of the f-block elements?
Quiz Answers:
1-The fundamental organizing principle of the modern periodic table is the atomic number.
2-There are seven periods in the modern periodic table.
3-The columns in the periodic table are known as groups or families.
4-The atomic number represents the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom and is the fundamental property used to arrange elements in the periodic table.
5-The alkali metals are found in Group 1 of the periodic table.
6-The noble gases are found in Group 18 of the periodic table.
7-Elements in the d-block are commonly referred to as transition metals.
8-The key property that differentiates elements in the f-block is their location below the main periodic table and their electron configurations.
9-The halogens are found in Group 17 of the periodic table.
10-The second series of the f-block elements is known as the actinides.
Quiz with answers
Here’s a multiple-choice quiz about the arrangement of elements in the modern periodic table, along with the correct answers:
Quiz Questions:
1-What is the primary organizing principle of the modern periodic table?
a) Atomic mass
b) Atomic number
c) Electron configuration
d) Alphabetical order
2-How many periods are there in the modern periodic table?
a) 4
b) 6
c) 7
d) 8
3-Which elements are found in Group 1 of the periodic table?
a) Noble gases
b) Halogens
c) Alkali metals
d) Alkaline earth metals
4-What is the term for elements in the d-block of the periodic table?
a) Transition metals
b) Alkali metals
c) Noble gases
d) Halogens
5-Which group contains the chemically inert and unreactive elements?
a) Group 1 (Alkali metals)
b) Group 2 (Alkaline earth metals)
c) Group 17 (Halogens)
d) Group 18 (Noble gases)
Quiz Answers:
1-b) Atomic number
The primary organizing principle of the modern periodic table is the atomic number, which represents the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
2-c) 7
There are seven periods in the modern periodic table, representing the number of electron shells in an atom.
3-c) Alkali metals
Group 1 of the periodic table contains the alkali metals, which are highly reactive elements.
4-a) Transition metals
Elements in the d-block of the periodic table are commonly referred to as transition metals due to their variable oxidation states and other properties.
5-d) Group 18 (Noble gases)
Group 18 contains the chemically inert and unreactive noble gases, which have full electron shells and are highly stable.
Quiz Questions:
1-Which group in the periodic table contains the alkaline earth metals?
a) Group 1
b) Group 2
c) Group 17
d) Group 18
2-Elements in the f-block are known for their placement below the main periodic table and are referred to as what?
a) Transition metals
b) Lanthanides and actinides
c) Halogens
d) Noble gases
3-The modern periodic table is primarily organized by:
a) Atomic mass
b) Number of neutrons
c) Atomic number
d) Electronegativity
4-Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of alkali metals?
a) Highly reactive with water
b) Form +1 cations
c) Found in Group 1 of the periodic table
d) Nonmetals
5-The elements in Group 17 of the periodic table are known as:
a) Alkali metals
b) Alkaline earth metals
c) Noble gases
d) Halogens
Quiz Answers:
1-b) Group 2
The alkaline earth metals are found in Group 2 of the periodic table.
2-b) Lanthanides and actinides
Elements in the f-block are known as lanthanides (first series) and actinides (second series), and they are located below the main periodic table.
3-c) Atomic number
The modern periodic table is primarily organized by atomic number, which represents the number of protons in the nucleus.
4-d) Nonmetals
Alkali metals are not nonmetals; they are highly reactive metals.
5-d) Halogens
Elements in Group 17 of the periodic table are known as halogens and include elements like fluorine, chlorine, and iodine.
Feel free to use these additional quiz questions to further test your knowledge or to help others learn about the arrangement of elements in the modern periodic table.
Quiz Questions:
1-Which block of elements in the periodic table is characterized by having their outermost electrons filling s-orbitals?
a) s-block
b) p-block
c) d-block
d) f-block
2-In the modern periodic table, which group contains elements that are highly reactive with water and oxygen, and tend to form +1 cations?
a) Group 2
b) Group 17
c) Group 18
d) Group 1
3-What is the primary reason that elements in the same group or family of the periodic table exhibit similar chemical properties?
a) They have the same atomic mass.
b) They have the same atomic radius.
c) They have the same electron configuration.
d) They have the same atomic number.
4-The transition metals are primarily found in which block of the periodic table?
a) s-block
b) p-block
c) d-block
d) f-block
5-Which group in the periodic table is known for its inert and chemically unreactive nature due to full electron shells?
a) Alkaline earth metals
b) Halogens
c) Noble gases
d) Alkali metals
Quiz Answers:
1-a) s-block
Elements with their outermost electrons filling s-orbitals are found in the s-block of the periodic table.
2-d) Group 1
Group 1, which contains alkali metals, is known for its highly reactive elements that tend to form +1 cations.
3-c) They have the same electron configuration.
Elements in the same group or family exhibit similar chemical properties because they have the same electron configuration and share the same number of valence electrons.
4-c) d-block
Transition metals are primarily found in the d-block of the periodic table.
5-c) Noble gases
Noble gases in Group 18 are known for their inert and chemically unreactive nature due to full electron shells.
Quiz Questions:
1-What is the term for the elements found in the second series of the f-block elements, located below the main periodic table?
a) Transition metals
b) Alkali metals
c) Lanthanides and actinides
d) Noble gases
2-Which element is typically used as the reference point for comparing atomic masses in the periodic table?
a) Hydrogen
b) Oxygen
c) Carbon
d) Helium
3-Elements in which group of the periodic table are known for readily forming -1 anions?
a) Alkali metals (Group 1)
b) Noble gases (Group 18)
c) Halogens (Group 17)
d) Alkaline earth metals (Group 2)
4-The f-block elements are characterized by having their outermost electrons filling which type of orbitals?
a) s-orbitals
b) p-orbitals
c) d-orbitals
d) f-orbitals
5-Which group in the periodic table is known for its metallic properties, including good electrical conductivity and malleability?
a) Halogens (Group 17)
b) Noble gases (Group 18)
c) Alkaline earth metals (Group 2)
d) Alkali metals (Group 1)
Quiz Answers:
1-c) Lanthanides and actinides
The second series of the f-block elements, found below the main periodic table, consists of lanthanides and actinides.
2-c) Carbon
Carbon is typically used as the reference point (with an atomic mass of 12) for comparing atomic masses in the periodic table.
3-c) Halogens (Group 17)
Halogens in Group 17 are known for readily forming -1 anions when they combine with other elements.
4-d) f-orbitals
The f-block elements have their outermost electrons filling f-orbitals.
5-c) Alkaline earth metals (Group 2)
Alkaline earth metals in Group 2 are known for their metallic properties, including good electrical conductivity and malleability.
Summary
This comprehensive lesson delves into the organization of elements in the modern periodic table, emphasizing the importance of the atomic number as the fundamental organizing principle. It covers key topics such as the arrangement of elements in rows and columns, the significance of valence electrons, and the distinct properties of alkali metals, noble gases, and transition metals. The s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block elements are explored, and periodic trends are discussed. This lesson serves as an informative resource for understanding the periodic table and the behavior of chemical elements.
