Organic chemistry and organic compounds
The organic chemistry and organic compounds
Berzelius
He divided all compounds into a- In organic compounds Coming from mineral source b- Organic Compound They are compounds that extracted from animal or plant origin.
Vital force theory
Berzelius considered that organic compound are formed by vital force which is found in living cells of the body and it is impossible to synthesized them in lab.
In 1828, The German scientist Wohler destroyed the vital force theory, when he prepared urea by heating an aqueous solution of two inorganic compounds, ammonium chloride and silver cyanate.
Organic chemistry focused on the study of carbon element with exception of carbon oxides, carbonate and cyanides salt.
The number of organic compounds are more than the organic ones.
The ratio between the organic and inorganic compounds is approximately 20: 1. there are more than 1000,000 organic compounds.
The abundance of organic compounds GR? is due to the ability of carbon atom to combine with itself or with others atoms by different kinds of bond, it might connect through single, double, triple bonds.

Carbon atoms can join together with different methods, either straight chains, branched chains, homocyclic or heterocyclic.

Notes
1-The number of covalent bonds around the atom indicates its valency
2- each single covalent bond represents on valency
3- each element in the organic compound has a specific and constant valency
Ex.

The differences between organic and inorganic compound:

comparison between the organic compounds and inorganic compounds
Chemical Structure:
Organic Compounds: Primarily composed of carbon and hydrogen, often with other elements like oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and halogens.
They typically have covalent bonds.
Inorganic Compounds: Comprise a wide range of elements, including metals, non-metals, and metalloids. They can have ionic or covalent bonds.
Solubility:
Organic Compounds: Often soluble in organic solvents like ethanol or acetone, but less soluble in water.
Inorganic Compounds: Solubility varies widely; some are highly soluble in water (e.g., salts), while others may be insoluble.
Melting and Boiling Points:
Organic Compounds: Generally lower melting and boiling points, but this can vary widely depending on molecular size and structure.
Inorganic Compounds: Tend to have higher melting and boiling points, especially for ionic compounds.
Inflammability:
Organic Compounds: Many organic compounds are flammable, especially hydrocarbons.
Inorganic Compounds: Generally less flammable, although exceptions exist.
Types of Bonds:
Organic Compounds: Primarily covalent bonds, including single, double, and triple bonds.
Inorganic Compounds: Can have ionic, covalent, metallic, or coordinate covalent bonds.
Conductivity:
Organic Compounds: Typically poor conductors of electricity.
Inorganic Compounds: Conductivity varies; ionic compounds in solution can conduct electricity, while covalent compounds generally do not.
Rate of Chemical Reaction:
Organic Compounds: Reactions can be relatively slow, influenced by factors like temperature and catalysts.
Inorganic Compounds: Rates vary widely; some reactions can be very fast, especially in the presence of water.
Polymerization:
Organic Compounds: Many organic compounds can undergo polymerization to form large, complex molecules (polymers).
Inorganic Compounds: While some inorganic compounds can polymerize, it is less common compared to organic compounds.
Isomerization:
Organic Compounds: Isomerization is common due to the presence of different arrangements of atoms.
Inorganic Compounds: Isomerization is less common, and isomers are often structural or geometric isomers in coordination compounds.
The molecular and structural formula of organic compounds
A- Molecular Formula:
It is the formula which indicates the number and kind of the elements which form the chemical compound, and doesn’t show the kind of the linkage between the atoms in the molecule
C2H4Cl2 C2H2 CH3OH
B- Structural Formula:
It’s the formula which indicates the number and kind of each element in the molecule, and the kind of linkage between the atoms by the covalent bonds.

Remember that The number of covalent bonds around the atom indicates its valency. Each single covalent bond represents one pair of valency.
Isomerism :
-many organic compounds are different in the physical and chemical properties and also in structural formula but they have the same molecular formula.
On writing the structural formula it seems the molecule has a planer shape, but in fact it has a stereo structure shape i.e. its atom is directed in 3 dimensions.

To illustrate the correct shape of the molecule, we must use the molecular formula
The structural formula show that the molecule has a stereo structure shape i.e. its atoms are directed in the three dimensions.
-Detection of carbon and hydrogen in organic compounds:
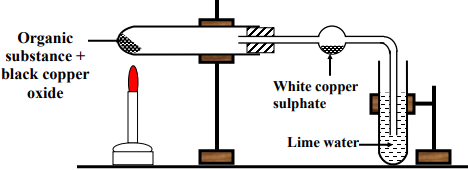
Procedure:
1- Heat organic compound with (CuO) in test tube
2- Pass the resulting gases over white anhydrous copper sulphate (CuSO4) then through clear lime water
Observations:
The white colour of anhydrous copper sulphate turns into blue which indicates the absorption of (CuSO4) to water vapor which is formed from combination of oxygen of CuO with the hydrogen of organic compound.
C + 2 CuO → 2 Cu + CO2
2H + CuO → Cu + H2O
Lime water turns turbid due to the evolution of carbon dioxide (CO2), which is formed from combination of oxygen of (CuO) with the carbon of the organic compound.
Conclusion:
The organic compound contains carbon and hydrogen.
C + 2 CuO → 2 Cu + CO2
2H + CuO → Cu + H2O
Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds consist of carbon and hydrogen only.
classification of Hydrocarbons

