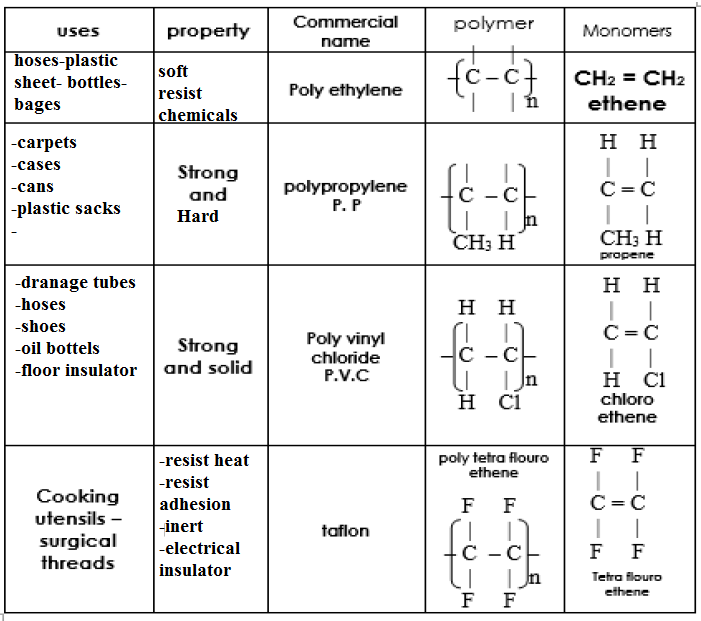
Ethylene :Ethene
Ethylene – Ethene C2H4
-It is the first member in the alkenes series
-The common name is :ethylene
Preparation of Ethene C2H4 in lab:
by removing water from ethyl alcohol (ethanol) by using hot concentrated sulphuric acid (H2SO4) at 180? C.
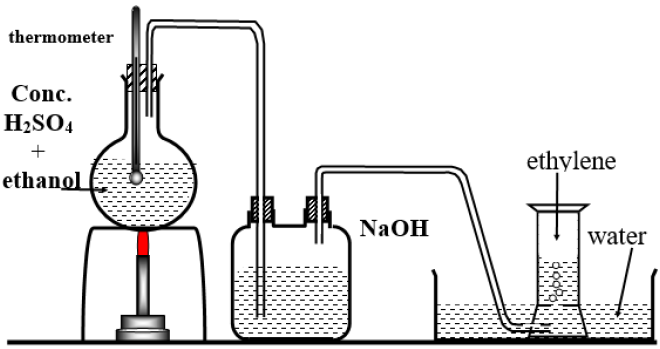

Give reasons?
1-Sodium hydroxide is used in preparation of Ethene in lab.?
-To eliminate the traces of fumes of concentrated sulphuric acid evolved with ethane gas
2-etheve gas is collected by downward displacement of water
-because ethane is lighter (les density )than water and it is insoluble in water
Physical properties of Alkenes:
Physical states Alkenes
1-Alenes contains 2 to 4 carbons atoms are gases
2-from 5 to 15 are liquids
3-more than 15 are solids
The solubility Alkenes :
They are nonpolar compounds don’t dissolve in polar solvents (water )but dissolves in organic solvents such as:
Ether – benzene – carbon tetrachloride
Chemical properties of alkenes
Alkenes are more active than alkane Give reason?
-Due to the weak pi bon which is easy to be broken while alkane contains strong sigma bond that is difficult to be broken
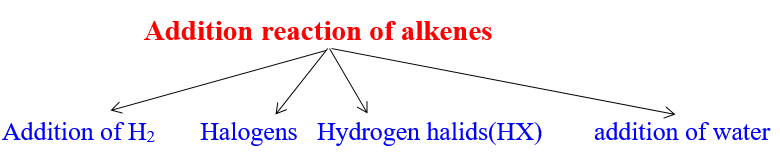
Reactions of Alkenes
1)Burning reaction of alkenes
2)Addition of alkenes
3) Oxidation of alkenes
4)polymerization reaction
1)Burning reaction(combustion):Exothermic reaction GR.?
-They are burn in air producing CO2 and water vapor and a lot of heat energy.
C2H4(g)+ 3O2(g) ⇒CO2(g) +2H2O(v) + energy
2)Addition reaction of Alkenes :
Addition of atom or atomic group to the carbon atom of double or triple bond to convert it into saturated compounds
Give reasons: addition reaction occurs in alkenes ? due to Pi bond that is easy to be broken.
1)addition reaction of H2 to alkenes(catalytic hydrogenation reaction)
Occurs in catalysts such as divided nickel of platinum with heating to form corresponding alkane

How to obtain alkane from alkene?
2)addition of halogen( X2) to alkene(Halogenation by addition)
– It is used in the detection of alkenes
Give reason: when passing ethene gas in bromine water(bromine dissolved in carbon tetrachloride) the red color of bromine disappears?
-because bromine breaks the double bond of ethane forming colorless 1,2-dibromoethane

Note:
-Alkenes halogenation reaction by addition don’t require ultraviolet rays (UV)
-Alkane halogenation reaction by substitution need Ultraviolet rays (UV)
write the symbolic equation to represent the chlorination of propene?

3)Addition of hydrogen halides (hydrolic acids HX) to alkenes :
This reaction depends on the type of alkenes if it is symmetric or asymmetric
Symmetric alkenes :
the 2 carbon atoms of the double bond carry the same number of hydrogen atoms
Ex: CH2 CH2
Asymmetric alkene:
the 2 carbon atoms of the double bond carry different numbers of hydrogen atoms
Ex: CH2 CH2
Asymmetric alkene: the 2 carbon atoms of the double bond carry different numbers of hydrogen atoms
EX: Propene

propene
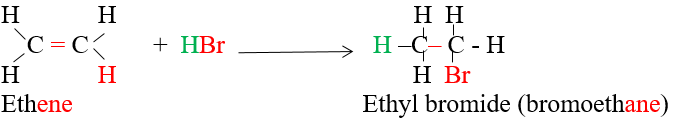
Addition of hydrogen halides to asymmetric alkenes:
The reactions take place according :Markownikoof s rule
Markownikoof s rule
on adding asymmetric reagent HX or (H-OSO3H) to an asymeric alkene the positive part of reagent is added to the carbon atom which carries the larger number of hydrogen atoms anf the negative part is added to the carbon which carries less number of hydrogen atoms.

Markownikoof s rule
Give reasons: adding hydrogen bromide to propene 1-bromopropane is not formed?
Due to Markownukoff s rule where when adding HBr to propene the (H+) is added the carbon with large number of hydrogen atoms while (Br-) is added to the carbon with small number of hydrogen atoms

Addition of water to alkenes (catalytic hydration)
Addition of water to alkene in presence of conc. Sulphuric acid as catalyst to form the corresponding alcohol

Addition of water to alkenes
Give reason:conc H2SO4 is used as a catalyst in ethane hydration reaction?
-because water is weak electrolyte so (H+) ions of water cant break the Pi bond so sulphuric acid increases the (H+) ions to break the Pi bond

Example:
write the symbolic equation which represents the catalytic hydration reaction of each of:
2-butene

3)Oxidation reactions
Alkenes are oxidized by the oxidizing agents like:
– hydrogen peroxide H2O2
-Alkaline purple potassium permanganate KMnO4 Forming dihydoxyl compound called Glycols
Baeyer ‘s reaction:
passing ethene gas in potassium permanganate solution the purple color is discharged and ethylene glycol is formed

Baeyer s reaction :is used to detect the presence of the double bond by discharging the purple color of permanganate
Importance of ethylene glycol :in radiators of cars as antifreezing to form hydrogen bond with water and to prevent formation of hydrogen bond between water molecules to prevent formation of ice crystal
Polymerization
The combination of large numbers of compounds molecules (monomers (from 100 to 1000000 molecules) to form a huge molecule called polymer

Method of polymerization
a)Addition polymerization
b)condensation polymerization
Addition polymerization:
Adding a huge number of unsaturated small molecules(monomers) to each other to form a very large saturated molecule(polymer)
Example1:
on heating ethene under high pressure (1000 atm) in presence of peroxides as initiators polyethylene is formed


Chloroethene monomers join together end-to-end to create poly(chloroethene), or commonly known as PVC. This can be seen in the image below:

Notes:The polymer formed by addition is:
1)similar to the monomer in the masses and empirical formula
2)different from the monomer in the molar mass ,the boiling point ,the density and the molecular formula
Example 5:
write the structural formulae of the polymers of :
Ethylene – propylene – chloroethene – tetrachloroethene