Iron as a Transition element, Extraction of Iron Element,properties of iron
Iron as a Transition element, Extraction of Iron Element,properties of iron
- Electronic configuration of Iron : Fe26 [Ar18]4s2,3d6
- it is found in a form of ore about 6.3% in earth crust
- The is a compound of Iron with impurities
- Iron differs from the other previous metals in the First transition series GR?
- It does not reach to the maximum oxidation state that is (+8) which caused by the removal of all its 8 valence electrons from (4s and 3d)
- The most important oxidation states for iron are Fe2+ and Fe3+
- Iron is the most important metal in heavy industries
- Iron found in the form of pure iron (90%) in meteorites only
Bases of choosing the Iron ore to extract of IRON :
1- % of impurities and their type
2-Poisonous impurities as P, As, and s Sulphur and how to get rid of them
3-% of Fe in Ore
What are the IRON Ores:
1-Haematite Fe2O3 (IRON III oxide)-blood red– 50-60%Fe(ASWAN)
2-Limonite: 2Fe2O3.3H2O (Hydrated Iron III Oxide)-20-60%Fe(Oasis)
3-Magnetic Iron Oxide Fe3O4 black Iron Oxide Magnetic Iron oxide-45-70%Fe(East desert)
4-Siderite FeCO3 yellow grey ( Iron II carbonate)-30-42%Fe

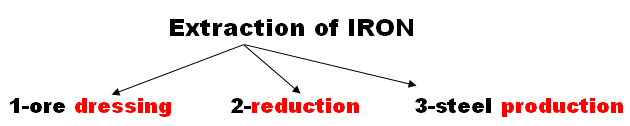
First : Dressing Ore:
1-ore dressing: by Crushing, sintering, concentrating, roasting
2-reduction: change the ore into Iron
3-steel production: to change the Iron(brittle) into steel Alloy (Iron and carbon which is more hardness )
What is the aim of ore dressing?
1)Improving physical properties :by crushing and sintering to get suitable size for reduction
1-crushing: to get ore with small size suitable for reduction
2-Sintering: collecting the iron ore particles getting from crushing or cleaning furnace in large size increase to be suitable for reduction
4-conentrating:
removing the unwanted impurities which chemically combined or mixed with ore by using surface tension property, magnetic or electrical separation
2)improving chemical properties: to get rid of impurities to increase Iron ore
How to improve the chemical properties?
By Roasting : heating of ore strongly in dry air to :
1)get rid of impurities by oxidation of (s) and (p)
2)expel humidity and
3)increase the % of Iron in Ore
a) expelling CO2 from the ore:

b)Expelling Humidity (H2O)
2Fe2O3.3H2O (40%) ⇒ 2Fe2O3 (69.6%) + 3H2O
c)oxidation of some impurities (S ,P)
1)Sulphur: S(s) + O2(g) ⇒ SO2(g)
2)phosphorous: 4P(s)+ 5SO2(g) ⇒ 2 P2O5 (g)
Second: reduction of IORN ore : by one of the 2 methods

The Iron produced from the furnace is so brittle and cannot use in industry
Third: steel production:
By 1)removing impurities resulted from furnace
2)Adding desirable element to get steel with desirable properties
That are done through 3 process: in 3 furnaces
1)electric furnace 2) open hearth furnace 3) oxygen converter
Properties of IRON 1) physical 2)chemical
1)Physical properties:
-Pure iron has no industrial importance GR?
Because it is relatively soft,low hardness malleable and ductile and has magnetic properties
-it melts at 1538 c ,it density is 7.87 gm/cm3
2)chemical properties of iron:
1)effect of air in iron: Red hot iron reacts with dry air(O2) giving magnetic iron oxide
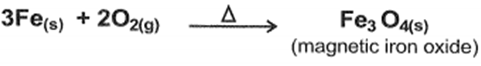
2)effect of water :red iron hot react with water vapor giving magnetic iron oxide and hydrogen

3)reaction with non- metals : iron react with chlorine gas giving iron(III)chloride(as chlorine is a strong oxidizing agent )

4) iron react with Sulphur giving iron(II) sulphide (as sulphur is a weak oxidizing agent)

5)Reaction with acids :
a)with diluted acids: Iron dissolves in dilute acids to form iron (II) salts and hydrogen GR?
-because hydrogen gas is reducing agent prevent formation of iron(III) salts:


b)with concentrated acids:–
Iron reacts with hot concentrated sulphuric acid to give :
Iron(II)sulphate ,iron(III) sulphate ,water and Sulphur dioxide gas:


G.R: Concentrated nitric acid HNO3 has a passivity effect on the iron ?
-Due to the formation of a non-porous layer of iron oxide which protects the metal from further reaction
-This layer can be removed by abrasion or by dilute hydrochloric acid HCl
-How can you convert iron metal into FeCl2 and FeCl3?
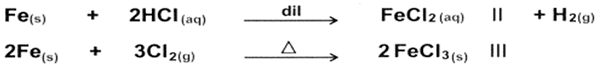
-How can you detect for Fe2+ and Fe3+?

Question: How can you get iron(II) hydroxide and iron(III)hydroxide
