CSS Font size Descriptions: A Comprehensive Guide Tutorial
CSS Font size Descriptions:
Here are some commonly used font size values in CSS along with their descriptions:
xx-small: |
Represents the smallest font size available in the browser’s font size scaling. |
x-small: |
Represents a smaller font size than the default font size. |
small: |
Represents a small font size compared to the default font size. |
medium: |
Represents the default font size in most browsers. |
large: |
Represents a larger font size compared to the default font size. |
x-large: |
Represents a larger font size than the default font size and larger than the large size. |
xx-large: |
Represents a larger font size than the default font size and larger than the x-large size. |
smaller: |
Represents a font size that is smaller than the parent element’s font size. |
larger: |
Represents a font size that is larger than the parent element’s font size. |
These font size values provide a range of options to control the size of text in CSS.
The values can be specified using keywords or length units such as pixels (px) or percentages (%).
Remember that font sizes can vary across different browsers and devices, so it’s essential to consider responsive design principles and test your web pages on various platforms to ensure optimal readability and user experience.
How to use the xx-small value for CSS font size?
xx-small: complete code in html
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates the usage of the xx-small value for font size in CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>xx-small Example</title>
<style>
p {
font-size: xx-small; /* Set font size to xx-small */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
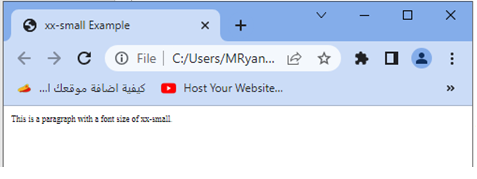
<p>This is a paragraph with a font size of xx-small.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In this example, we have applied the xx-small value to the font size of the p element.
2-The xx-small value represents the smallest font size available in the browser’s font size scaling.
3-It is typically smaller than the default font size.
You can save this code in an HTML file and open it in a web browser to see the rendered text with the specified font size.
Try to modify the HTML structure and add additional content to experiment with the xx-small font size value in different contexts.
How to use the x-small value for CSS font size?
x-small: complete code in html
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates the usage of the x-small value for font size in CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>x-small Example</title>
<style>
p {
font-size: x-small; /* Set font size to x-small */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
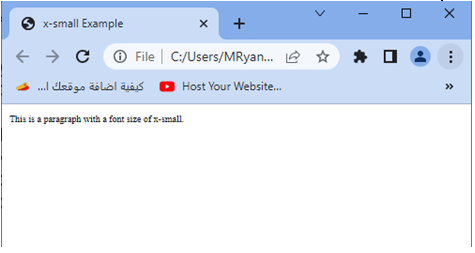
<p>This is a paragraph with a font size of x-small.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In this example, we have applied the x-small value to the font size of the p element.
2-The x-small value represents a smaller font size than the default font size, but larger than the xx-small size.
You can save this code in an HTML file and open it in a web browser to see the rendered text with the specified font size.
Try to modify the HTML structure and add additional content to experiment with the x-small font size value in different contexts.
How to use the small value for CSS font size?
small: complete code in html
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates the usage of the small value for font size in CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>small Example</title>
<style>
p {
font-size: small; /* Set font size to small */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
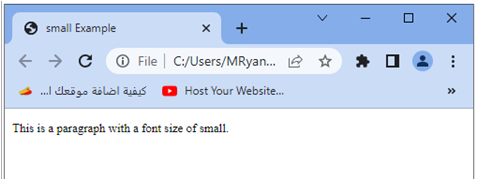
<p>This is a paragraph with a font size of small.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In this example, we have applied the small value to the font size of the p element.
2-The small value represents a smaller font size compared to the default font size.
You can save this code in an HTML file and open it in a web browser to see the rendered text with the specified font size.
Try to modify the HTML structure and add additional content to experiment with the small font size value in different contexts.
How to use the medium value for CSS font size?
medium: complete code in html
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates the usage of the medium value for font size in CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>medium Example</title>
<style>
p {
font-size: medium; /* Set font size to medium */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
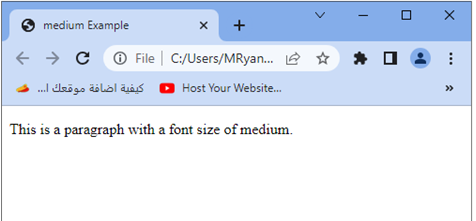
<p>This is a paragraph with a font size of medium.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In this example, we have applied the medium value to the font size of the p element.
2-The medium value represents the default font size in most browsers.
You can save this code in an HTML file and open it in a web browser to see the rendered text with the specified font size.
Try to modify the HTML structure and add additional content to experiment with the medium font size value in different contexts.
How to use the large value for CSS font size ?
large: complete code in html
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates the usage of the large value for font size in CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>large Example</title>
<style>
p {
font-size: large; /* Set font size to large */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
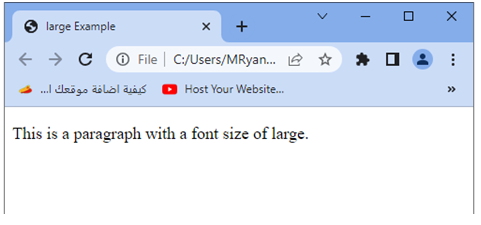
<p>This is a paragraph with a font size of large.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In this example, we have applied the large value to the font size of the p element.
2-The large value represents a larger font size compared to the default font size.
You can save this code in an HTML file and open it in a web browser to see the rendered text with the specified font size.
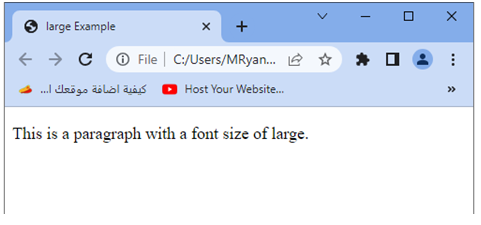
Try to modify the HTML structure and add additional content to experiment with the large font size value in different contexts.
How to use the x-large value for CSS font size ?
x-large: complete code in html
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates the usage of the x-large value for font size in CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>x-large Example</title>
<style>
p {
font-size: x-large; /* Set font size to x-large */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is a paragraph with a font size of x-large.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In this example, we have applied the x-large value to the font size of the p element.
2-The x-large value represents a larger font size compared to the default font size and larger than the large size.
You can save this code in an HTML file and open it in a web browser to see the rendered text with the specified font size.
Try to modify the HTML structure and add additional content to experiment with the x-large font size value in different contexts.
How to use the xx-large value for CSS font size ?
xx-large: complete code in html
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates the usage of the xx-large value for font size in CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>xx-large Example</title>
<style>
p {
font-size: xx-large; /* Set font size to xx-large */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is a paragraph with a font size of xx-large.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In this example, we have applied the xx-large value to the font size of the p element.
2-The xx-large value represents a larger font size compared to the default font size and larger than the x-large size.
You can save this code in an HTML file and open it in a web browser to see the rendered text with the specified font size.
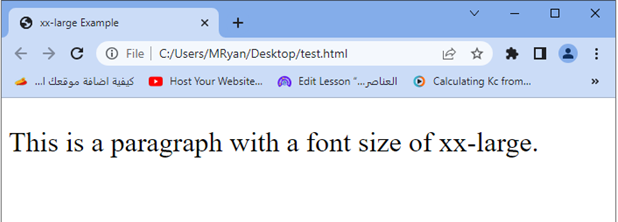
Try to modify the HTML structure and add additional content to experiment with the xx-large font size value in different contexts.
How to use the smaller value for CSS font size ?
smaller: complete code in html
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates the usage of the smaller value for font size in CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>smaller Example</title>
<style>
p {
font-size: smaller; /* Set font size to smaller */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is a paragraph with a font size of smaller.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In this example, we have applied the smaller value to the font size of the p element.
2-The smaller value represents a font size that is smaller than the parent element’s font size.
You can save this code in an HTML file and open it in a web browser to see the rendered text with the specified font size.
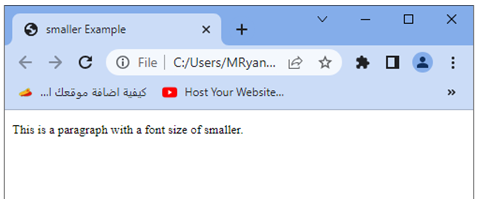
Try to modify the HTML structure and add additional content to experiment with the smaller font size value in different contexts.
How to use the larger value for CSS font size?
larger: complete code in html
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates the usage of the larger value for font size in CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>larger Example</title>
<style>
p {
font-size: larger; /* Set font size to larger */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is a paragraph with a font size of larger.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In this example, we have applied the larger value to the font size of the p element.
2-The larger value represents a font size that is larger than the parent element’s font size.
You can save this code in an HTML file and open it in a web browser to see the rendered text with the specified font size.

Try to modify the HTML structure and add additional content to experiment with the larger font size value in different contexts.
How to use pixels and percentages for CSS font size?
size in pixels or %:complete code in html
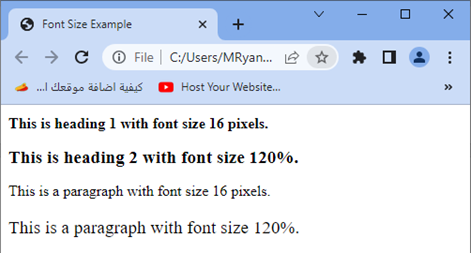
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates the usage of font size in pixels and percentages:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Font Size Example</title>
<style>
.pixel-size {
font-size: 16px; /* Set font size in pixels */
}
.percentage-size {
font-size: 120%; /* Set font size in percentage */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="pixel-size">This is heading 1 with font size 16 pixels.</h1>
<h2 class="percentage-size">This is heading 2 with font size 120%.</h2>
<p class="pixel-size">This is a paragraph with font size 16 pixels.</p>
<p class="percentage-size">This is a paragraph with font size 120%.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In this example, we have defined two CSS classes: pixel-size and percentage-size.
2-The pixel-size class sets the font size to 16 pixels, while the percentage-size class sets the font size to 120% of the parent element’s font size.
You can save this code in an HTML file and open it in a web browser to see the rendered text with the specified font sizes.
Try to modify the pixel size and percentage values in the CSS classes to experiment with different font sizes in pixels and percentages.
