CSS Text Properties: A Comprehensive Guide to Styling Text in CSS
CSS Text Properties
Learn about CSS text properties and how to style text in CSS. Explore, CSS text properties, styling text in CSS, text color, text alignment, text direction, text indentation, line height, whitespace handling.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) provides various properties and values to style and format text on web pages.
Here are some commonly used CSS text properties:
CSS text color:
Sets the color of the text. You can use predefined color names, RGB values, or hexadecimal color codes.
Example:
color: red; color: rgb(255, 0, 0); color: #FF0000;
CSS font-family:
Specifies the font used for the text. You can specify multiple fonts separated by commas, and the browser will use the first available font.
Example
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
CSS font-size:
Sets the size of the text. You can specify the size in pixels, points, ems, or percentages.
Example:
font-size: 16px; font-size: 1.2em;
CSS font-weight:
Sets the weight (thickness) of the text.
Common values are normal (default), bold, bolder, lighter, or numeric values.
Example:
font-weight: bold; font-weight: 700;
CSS text-align:
Specifies the alignment of the text within its container.
Common values are left, right, center, or justify.
Example:
text-align: center;
CSS text-decoration:
Adds visual effects to the text, such as underline, overline, line-through, or none.
Example:
text-decoration: underline;
CSS text-transform:
Changes the capitalization of the text.
Common values are none (default), uppercase, lowercase, or capitalize.
Example:
text-transform: uppercase;
CSS line-height:
Sets the height of a line of text. You can specify it as a number, a percentage, or using normal.
Example:
line-height: 1.5; line-height: 150%;
CSS letter-spacing:
Adjusts the spacing between characters in the text.
Example:
letter-spacing: 1px;
There are many more properties available to control the appearance and behavior of text on web pages.
How to set the CSS text properties on HTML elements?
Here’s a complete HTML code example that incorporates some of the CSS text properties mentioned earlier:
Step by step:
1)step one: open the notepad text Editor then write the following code :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Text Example</title>
<style>
/* CSS styles */
.my-text {
color: red;
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
font-size: 24px;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: underline;
text-transform: uppercase;
line-height: 1.5;
letter-spacing: 1px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="my-text">Hello, CSS Text!</h1>
<p class="my-text">This is an example of styled text using CSS properties.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have defined a CSS style with the class .my-text that applies various text properties.
2-The h1 and p elements in the HTML body use this class to apply the specified styles.
3- the following css text properties are applied to p ,and h1 elements:
- color: red;
- font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
- font-size: 24px;
- font-weight: bold;
- text-align: center;
- text-decoration: underline;
- text-transform: uppercase;
- line-height: 1.5;
- letter-spacing: 1px;
2)step 2: save the file with name:test.html
3)step 3: open the test.html file by any web browser to see th following results:
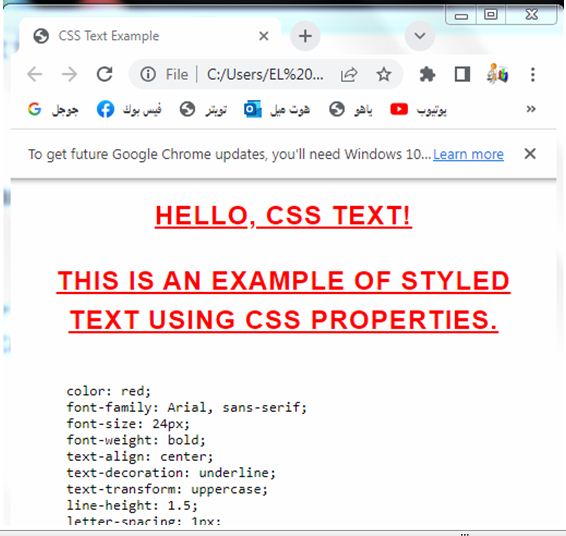
Try to adjust the CSS properties and content to see the visual changes in the displayed text.
How to set CSS text color on HTML elements ?
CSS text color
In CSS, you can set the color of text using the color property.
Here are different ways to specify the color in CSS:
By Predefined color names:
CSS provides a set of predefined color names that you can use directly.
Some common color names are red, blue, green, black, white, etc.
Example:
color: red; color: blue;
By RGB values:
You can specify the color using RGB values. RGB stands for Red, Green, and Blue, and each component can have a value between 0 and 255.
This allows you to create custom colors.
Example:
color: rgb(255, 0, 0); /* red */ color: rgb(0, 0, 255); /* blue */ color: rgb(255, 255, 0); /* yellow */
By Hexadecimal color codes:
Another way to specify custom colors is by using hexadecimal color codes.
Hex codes start with a # followed by a six-digit combination of numbers (0-9) and letters (A-F).
Each pair of digits represents the intensity of red, green, and blue, respectively.
Example:
color: #FF0000; /* red */ color: #0000FF; /* blue */ color: #FFFF00; /* yellow */
By RGBA values:
RGBA is similar to RGB, but with an additional alpha channel that represents the opacity of the color.
The alpha value ranges from 0 (fully transparent) to 1 (fully opaque).
Example:
color: rgba(255, 0, 0, 0.5); /* semi-transparent red */
By HSL and HSLA values:
HSL stands for Hue, Saturation, and Lightness.
It provides an alternative way to define colors based on hue, saturation, and lightness values.
HSLA is similar to HSL but includes an alpha channel for opacity.
Example:
color: hsl(0, 100%, 50%); /* red */ color: hsla(0, 100%, 50%, 0.5); /* semi-transparent red */
These are some of the common ways to set the text color in CSS.
Choose the method that suits your needs and apply it to the desired element or class using the color property.
The CSS text color complete example
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates setting the text color using CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Text Color Example</title>
<style>
/* CSS styles */
.red-text {
color: red;
}
.blue-text {
color: blue;
}
.custom-text {
color: rgb(255, 0, 255); /* Magenta */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="red-text">This heading is in red</h1>
<p class="blue-text">This paragraph is in blue</p>
<p class="custom-text">This paragraph has a custom color (magenta)</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have defined three CSS classes: .red-text, .blue-text, and .custom-text.
2-Each class sets the color property to a specific value.
3-The <h1> element uses the red-text class, the first <p> element uses the blue-text class, and the second <p> element uses the custom-text class.
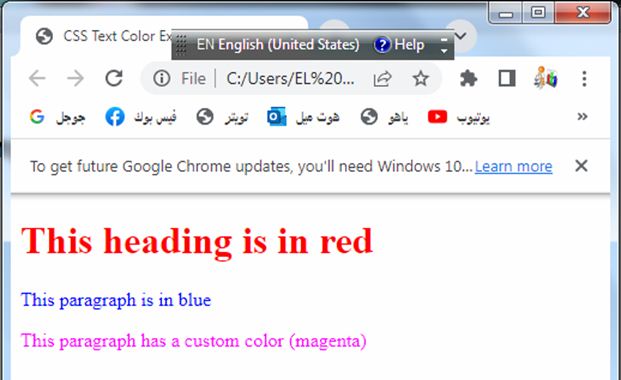
Try to modify the colors and add more text elements with different classes to see how the text color changes.
Text Color and Background Color
How to apply CSS text Color and background color on HTML elements?
Here’s an updated version of the HTML code that demonstrates setting both text color and background color using CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Text and Background Color Example</title>
<style>
/* CSS styles */
.red-text {
color: red;
background-color: yellow;
}
.blue-text {
color: blue;
background-color: lightgray;
}
.custom-text {
color: #FFFFFF; /* White text color */
background-color: #FF00FF; /* Magenta background color */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="red-text">This heading has red text on a yellow background</h1>
<p class="blue-text">This paragraph has blue text on a light gray background</p>
<p class="custom-text">This paragraph has white text on a magenta background</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the updated code, the CSS classes .red-text, .blue-text, and .custom-text have been modified to include both the color property for text color and the background-color property for background color.
2-Each class now sets a specific combination of text and background colors.
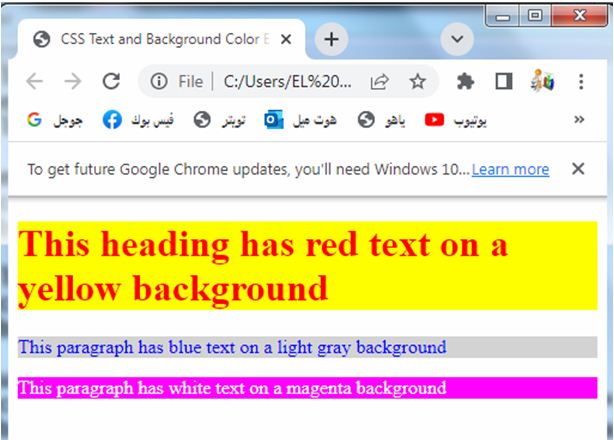
You can modify the colors using predefined color names, RGB values, or hexadecimal color codes to achieve the desired effect.
Try to experiment with different colors and apply them to different elements or classes.
How to apply CSS Text Alignment on HTML elements ?
CSS Text Alignment
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates CSS text alignment:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Text Alignment Example</title>
<style>
/* CSS styles */
.left-align {
text-align: left;
}
.right-align {
text-align: right;
}
.center-align {
text-align: center;
}
.justify-align {
text-align: justify;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="left-align">This heading is left-aligned</h1>
<p class="right-align">This paragraph is right-aligned</p>
<p class="center-align">This paragraph is center-aligned</p>
<p class="justify-align">This paragraph is justified. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Donec at viverra purus. Pellentesque sagittis elit sit amet eros cursus, et malesuada mauris interdum. Sed sed tortor et dolor feugiat laoreet sed vitae arcu.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have defined four CSS classes: .left-align, .right-align, .center-align, and .justify-align. Each class sets the text-align property to a specific value.
2-The left-align class aligns the text to the left.
3-The right-align class aligns the text to the right.
4-The center-align class centers the text horizontally.
5-The justify-align class justifies the text, meaning it adjusts the spacing between words to align both the left and right edges.
6-The <h1> element uses the left-align class, the first <p> element uses the right-align class, the second <p> element uses the center-align class, and the third <p> element uses the justify-align class.
Try to modify the classes and add more text elements with different classes to see how the text alignment changes based on the text-align property you assign to each class.
How to apply Text Alignment and Text Direction on HTML elements?
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates CSS text alignment and text direction:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Text Alignment and Direction Example</title>
<style>
/* CSS styles */
.left-align {
text-align: left;
}
.right-align {
text-align: right;
}
.center-align {
text-align: center;
}
.justify-align {
text-align: justify;
}
.rtl-text {
direction: rtl;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="left-align">This heading is left-aligned</h1>
<p class="right-align">This paragraph is right-aligned</p>
<p class="center-align">This paragraph is center-aligned</p>
<p class="justify-align">This paragraph is justified. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Donec at viverra purus. Pellentesque sagittis elit sit amet eros cursus, et malesuada mauris interdum. Sed sed tortor et dolor feugiat laoreet sed vitae arcu.</p>
<p class="rtl-text">This paragraph has right-to-left text direction. مرحبا بك في العالم</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have added a new CSS class .rtl-text that sets the direction property to rtl for right-to-left text direction.
2-The updated code includes the following CSS classes:
.left-align aligns the text to the left.
.right-align aligns the text to the right.
.center-align centers the text horizontally.
.justify-align justifies the text, adjusting the spacing between words to align both the left and right edges.
.rtl-text sets the right-to-left text direction.
3-The examples provided include both text alignment and text direction.
4-The heading and paragraphs are aligned based on the text-align property, while the paragraph with the .rtl-text class has its text direction set to right-to-left.
Try to modify the classes, add more text elements with different classes, and explore further combinations of text alignment and direction.
Properties of Text Alignment and Text Direction
Here are the properties related to text alignment and text direction in CSS:
text-align:
Specifies the horizontal alignment of text within its container.
Common values are left, right, center, and justify.
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates different text alignments using CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Text Alignment Example</title>
<style>
/* CSS styles */
.left-align {
text-align: left;
}
.right-align {
text-align: right;
}
.center-align {
text-align: center;
}
.justify-align {
text-align: justify;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="left-align">This heading is left-aligned</h1>
<p class="right-align">This paragraph is right-aligned</p>
<p class="center-align">This paragraph is center-aligned</p>
<p class="justify-align">This paragraph is justified. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Donec at viverra purus. Pellentesque sagittis elit sit amet eros cursus, et malesuada mauris interdum. Sed sed tortor et dolor feugiat laoreet sed vitae arcu.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have defined four CSS classes: .left-align, .right-align, .center-align, and .justify-align.
2-Each class sets the text-align property to a specific value.
The left-align class aligns the text to the left.
The right-align class aligns the text to the right.
The center-align class centers the text horizontally.
The justify-align class justifies the text, meaning it adjusts the spacing between words to align both the left and right edges.
3-The <h1> element uses the left-align class, the first <p> element uses the right-align class, the second <p> element uses the center-align class, and the third <p> element uses the justify-align class.
Try to modify the classes and add more text elements with different classes to see how the text alignment changes based on the text-align property you assign to each class.
Text Direction:
Sets the direction of text.
Common values are ltr (left-to-right) and rtl (right-to-left).
This property is especially useful for languages that are written from right to left, such as Arabic or Hebrew.
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates text direction using CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Text Direction Example</title>
<style>
/* CSS styles */
.rtl-text {
direction: rtl;
}
.ltr-text {
direction: ltr;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="rtl-text">مرحبا بك في العالم</p>
<p class="ltr-text">Hello, World!</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have defined two CSS classes: .rtl-text and .ltr-text.
2-Each class sets the direction property to a specific value.
The rtl-text class sets the text direction to right-to-left.
The ltr-text class sets the text direction to left-to-right (the default direction).
The first paragraph (<p>) uses the rtl-text class, displaying text from right to left. The second paragraph uses the ltr-text class, displaying text from left to right.
Try to modify the classes and add more paragraphs with different classes to see how the text direction changes based on the direction property you assign to each class.
Vertical Alignment:
Controls the vertical alignment of inline or table-cell elements within a line or cell. It can be set to values like baseline, top, middle, bottom, text-top, or text-bottom.
Vertical alignment is typically applied to inline or table-cell elements within a line or cell.
However, if you are looking for vertical alignment within a container, such as aligning a single line of text vertically within a div, you can achieve it using CSS Flexbox.
Here’s an example of how to vertically align text within a container using Flexbox:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Vertical Alignment Example</title>
<style>
/* CSS styles */
.container {
display: flex;
align-items: center; /* Vertical alignment */
height: 200px; /* Height of the container */
border: 1px solid black; /* Just for demonstration */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<p>This text is vertically aligned within the container</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we create a container div with the class container.
2-We set the display property to flex to enable flexbox behavior.
3-The align-items property is set to center, which vertically aligns the flex items (in this case, the <p> element) within the container.
4-The container has a height of 200px (you can adjust it as needed) and a border to visualize its boundaries.
You can modify the content of the container, change the height, or apply the container class to different elements to see how the text is vertically aligned within the container using Flexbox.
Text Indentation:
text-indent:
Specifies the indentation of the first line of text within an element. It can be set to a specific length (e.g., 20px) or a percentage (e.g., 2em).
Line Height:
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates text indentation using
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Text Indentation Example</title>
<style>
/* CSS styles */
.indented-text {
text-indent: 2em;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="indented-text">This paragraph has an indentation of 2em. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Donec at viverra purus. Pellentesque sagittis elit sit amet eros cursus, et malesuada mauris interdum. Sed sed tortor et dolor feugiat laoreet sed vitae arcu.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have defined a CSS class called .indented-text.
2-The text-indent property is set to 2em, which indicates an indentation of two times the size of the current font.
3-The .indented-text class is applied to the <p> element.
4-The paragraph will have an indentation of 2em from the left side of the container.
You can adjust the text-indent value as needed to increase or decrease the indentation.
Try to modify the class name and the content of the paragraph to see how the text indentation changes when you apply different values to the text-indent property.
Line Height:
Sets the height of a line of text. It can be set to a specific length, a percentage, or the normal keyword.
White Space Handling:
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates line height using CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Line Height Example</title>
<style>
/* CSS styles */
.custom-line-height {
line-height: 1.5;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>This paragraph has the default line height.</p>
<p class="custom-line-height">This paragraph has a custom line height of 1.5.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have defined a CSS class called .custom-line-height. The line-height property is set to 1.5.
2-The .custom-line-height class is applied to the second <p> element.
3-The first paragraph will have the default line height, which is typically around 1.2 to 1.4, depending on the browser and default styles.
4-The second paragraph will have a custom line height of 1.5 times the height of the font. This means that the lines of text will be spaced further apart, creating more vertical space between lines.
Try to modify the class name and the value of the line-height property to experiment with different line heights and see how it affects the spacing between lines of text.
White Space Handling:
white-space:
Defines how white space characters are handled within an element.
Common values are normal (collapses multiple spaces into one), nowrap (prevents line breaks within the element), and pre (preserves white space formatting).
These properties allow you to control the alignment, direction, indentation, and spacing of text within HTML elements.
You can use them individually or in combination to achieve the desired text layout and presentation on your web page.
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates white space handling using CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS White Space Handling Example</title>
<style>
/* CSS styles */
.normal-white-space {
white-space: normal;
}
.no-wrap-white-space {
white-space: nowrap;
}
.pre-white-space {
white-space: pre;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="normal-white-space">This paragraph has normal white space handling. Multiple spaces are collapsed.</p>
<p class="no-wrap-white-space">This paragraph has nowrap white space handling. Multiple spaces are preserved.</p>
<p class="pre-white-space">This paragraph has pre white space handling. Multiple spaces and line breaks are preserved.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have defined three CSS classes: .normal-white-space, .no-wrap-white-space, and .pre-white-space.
2-Each class sets the white-space property to a specific value.
3-The normal-white-space class sets the white-space property to normal, which collapses multiple consecutive spaces into a single space.
4-The no-wrap-white-space class sets the white-space property to nowrap, which preserves multiple consecutive spaces.
5-The pre-white-space class sets the white-space property to pre, which preserves both multiple spaces and line breaks.
6-The first paragraph uses the normal-white-space class, the second paragraph uses the no-wrap-white-space class, and the third paragraph uses the pre-white-space class.
Try to modify the classes and the content of the paragraphs to see how different white space handling affects the spacing and rendering of the text.
Text Align Last:
The text-align-last property in CSS is used to specify the alignment of the last line of a block of text. However, note that it is not widely supported by all browsers.
Here’s an example of the complete HTML code that demonstrates the text-align-last property:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS Text Align Last Example</title>
<style>
/* CSS styles */
.align-last {
text-align-last: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
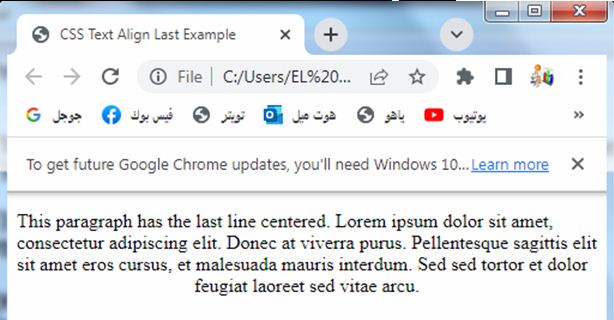
<p class="align-last">This paragraph has the last line centered. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Donec at viverra purus. Pellentesque sagittis elit sit amet eros cursus, et malesuada mauris interdum. Sed sed tortor et dolor feugiat laoreet sed vitae arcu.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have defined a CSS class called .align-last.
2-The text-align-last property is set to center.
3-The .align-last class is applied to the <p> element.
4-The paragraph will have the last line centered.
However, note that the text-align-last property may not be supported by all browsers, particularly older versions. In such cases, the alignment may not take effect, and the text will remain left-aligned.
Try to modify the class name and the value of the text-align-last property to experiment with different alignment options and see how it affects the alignment of the last line of the text.
unicode-bidi:
Here’s a complete HTML code example that demonstrates the unicode-bidi property in CSS:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>CSS unicode-bidi Example</title>
<style>
/* CSS styles */
.rtl-text {
unicode-bidi: bidi-override;
direction: rtl;
}
.ltr-text {
unicode-bidi: bidi-override;
direction: ltr;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
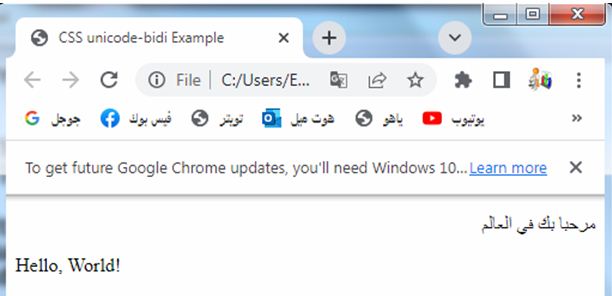
<p class="rtl-text">مرحبا بك في العالم</p>
<p class="ltr-text">Hello, World!</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have defined two CSS classes: .rtl-text and .ltr-text.
2-Both classes use the unicode-bidi property with the value bidi-override.
3-This property enables explicit control over the bidirectional behavior of text.
4-We also set the direction property to rtl for the .rtl-text class and ltr for the .ltr-text class.
5-The first paragraph (<p>) uses the .rtl-text class, displaying right-to-left text (in this case, Arabic).
6-The second paragraph uses the .ltr-text class, displaying left-to-right text (in this case, English).
7-The unicode-bidi: bidi-override; declaration is necessary to ensure proper bidirectional rendering of text. It overrides the default behavior and allows explicit control over the text direction.
Try to modify the classes and the text content to see how the unicode-bidi property affects the bidirectional rendering of text.
Quiz with answers about this lesson without web page
Here’s a multi-choice quiz about CSS text properties:
1-Which CSS property is used to change the color of text?
a) font-color
b) text-color
c) color
d) text-style
Answer: c) color
2-How can you align text to the right in CSS?
a) text-align: right
b) text-align: center
c) text-align: left
d) text-align: justify
Answer: a) text-align: right
3-Which property is used to control the direction of text?
a) text-align
b) direction
c) text-direction
d) text-orientation
Answer: b) direction
4-What property can be used to indent the first line of a text block?
a) text-indent
b) text-spacing
c) text-wrap
d) text-align
Answer: a) text-indent
5-How can you adjust the spacing between lines of text?
a) text-spacing
b) line-spacing
c) line-height
d) text-line
Answer: c) line-height
5-Which property is used to handle white space within text?
a) text-collapse
b) text-space
c) white-space
d) text-wrap
Answer: c) white-space
7-How can you align the last line of a text block?
a) text-align-last
b) align-last
c) text-align-end
d) text-last-line
Answer: a) text-align-last
8-Which property controls the bidirectional behavior of text?
a) text-direction
b) directionality
c) unicode-bidi
d) bidirectional
Answer: c) unicode-bidi
9-How can you make text bold in CSS?
a) text-weight: bold
b) font-weight: bold
c) text-decoration: bold
d) text-style: bold
Answer: b) font-weight: bold
10-Which CSS property is used to control the spacing between letters in text?
a) letter-spacing
b) text-spacing
c) word-spacing
d) text-indent
Answer: a) letter-spacing
11-How can you make text italic in CSS?
a) text-style: italic
b) font-style: italic
c) text-decoration: italic
d) font-decoration: italic
Answer: b) font-style: italic
12-Which property can be used to control the capitalization of text?
a) text-transform
b) text-decoration
c) font-variant
d) text-style
Answer: a) text-transform
13-How can you add an underline to text in CSS?
a) text-decoration: underline
b) text-decoration: line-through
c) text-decoration: overline
d) text-decoration: none
Answer: a) text-decoration: underline
14-Which property is used to control the spacing between words in text?
a) word-spacing
b) text-spacing
c) letter-spacing
d) word-wrap
Answer: a) word-spacing
15-How can you make text appear in uppercase letters in CSS?
a) text-transform: lowercase
b) text-transform: capitalize
c) text-transform: uppercase
d) text-transform: none
Answer: c) text-transform: uppercase
16-Which property is used to control the spacing between characters in a text block?
a) text-spacing
b) line-spacing
c) letter-spacing
d) word-spacing
Answer: c) letter-spacing
17-How can you control the visibility of text decorations like underline or line-through in CSS?
a) text-decoration-color
b) text-decoration-style
c) text-decoration-line
d) text-decoration
Answer: d) text-decoration
18-Which property is used to control the thickness of the text stroke in CSS?
a) text-outline-width
b) text-stroke-width
c) text-stroke
d) text-outline
Answer: c) text-stroke
19-How can you control the visibility of text overflow in CSS?
a) text-overflow
b) overflow-text
c) text-wrap
d) overflow
Answer: a) text-overflow
20-Which property is used to apply a shadow effect to text in CSS?
a) text-shadow
b) box-shadow
c) text-effect
d) shadow-effect
Answer: a) text-shadow
21-How can you control the spacing between lines of text without affecting the line breaks?
a) line-spacing
b) line-height
c) text-spacing
d) text-line
Answer: b) line-height
22-Which CSS property is used to control the wrapping behavior of long words and URLs in text?
a) word-wrap
b) text-wrap
c) overflow-wrap
d) white-space
Answer: c) overflow-wrap
23-How can you make text have an uppercase first letter in CSS?
a) text-transform: lowercase
b) text-transform: capitalize
c) text-transform: uppercase-first
d) text-transform: none
Answer: b) text-transform: capitalize
24-Which property is used to control the alignment of text within its container vertically?
a) text-align
b) vertical-align
c) text-vertical-align
d) align-content
Answer: b) vertical-align
25-How can you control the spacing between consecutive words in a text block?
a) text-spacing
b) word-spacing
c) letter-spacing
d) line-spacing
Answer: b) word-spacing
26-Which property is used to control the visibility of text overflow when it exceeds the specified width of its container?
a) text-wrap
b) text-overflow
c) word-wrap
d) word-overflow
Answer: b) text-overflow
27-How can you control the alignment of a block of text both horizontally and vertically within its container?
a) text-align
b) vertical-align
c) align-content
d) text-vertical-align
Answer: c) align-content
28-Which CSS property is used to apply a specific font family to a block of text?
a) font-family
b) text-family
c) font-style
d) text-style
Answer: a) font-family
29-How can you control the visibility of text decorations like underline or line-through only for specific parts of the text in CSS?
a) text-decoration-color
b) text-decoration-style
c) text-decoration-line
d) text-decoration-skip
Answer: c) text-decoration-line
30-Which property is used to control the visibility and style of the line that appears below or above text in CSS?
a) text-decoration
b) text-line
c) text-border
d) text-underline
Answer: a) text-decoration
31-Which property is used to control the alignment of text within its container when it spans multiple lines?
a) text-align-last
b) text-align
c) text-justify
d) text-align-multi
Answer: c) text-justify
How can you control the visibility of hyphenation in text when it exceeds the specified width of its container?
a) hyphenate
b) text-overflow
c) text-hyphen
d) overflow-wrap
Answer: d) overflow-wrap
32-Which property is used to apply a gradient color effect to the text in CSS?
a) text-gradient
b) color-gradient
c) text-fill
d) text-fill-color
Answer: d) text-fill-color
33-How can you control the visibility of the first line of text within a block differently from the rest of the text?
a) text-first-line
b) first-line
c) first-line-style
d) text-indent
Answer: b) first-line
34-Which CSS property is used to control the spacing between consecutive letters in text?
a) word-spacing
b) text-spacing
c) letter-spacing
d) text-indent
Answer: c) letter-spacing
