CSS Text Transformation: A Guide to Styling and Formatting Text
CSS Text Transformation
Learn about the CSS text-transform property and how it can be used to style and format text in HTML.
Explore various transformations such as CSS text-transform, text formatting, CSS properties, styling text in HTML, text formatting in CSS, uppercase and lowercase text, capitalize first letter, CSS text transformation examples
What specific transformation are you looking for? Do you want to convert text to uppercase, lowercase, title case, or something else? Please provide more details so I can assist you better.
The CSS Text Transformation Property
In CSS, you can apply various text transformations using the text-transform property.
This property allows you to change the capitalization or case of text.
The CSS text-transform property is used to specify the capitalization or case transformation of text within an element.
Here are the different values you can use with text-transform:
none |
This is the default value and indicates that no capitalization or case transformation should be applied. |
capitalize |
This value capitalizes the first character of each word. |
uppercase |
This value converts all characters to uppercase. |
lowercase |
This value converts all characters to lowercase. |
initial |
This value sets the capitalization or case transformation to its initial value, which may vary depending on the browser or user agent. |
inherit |
This value inherits the capitalization or case transformation from its parent element. |
Here’s an example of how you can use the text-transform property in CSS:
h1 {
text-transform: uppercase;
}
p {
text-transform: capitalize;
}
2-You can apply the text-transform property to various HTML elements such as headings (<h1>, <h2>, etc.), paragraphs (<p>), or any other elements that contain text.
Note that the text-transform property affects only the visual rendering of the text and does not modify the underlying content or affect its behavior.
capitalize: complete code in html
Here’s an example of how you can use the text-transform: capitalize; property in HTML and CSS to capitalize the first letter of each word in a paragraph:
Do the following steps:
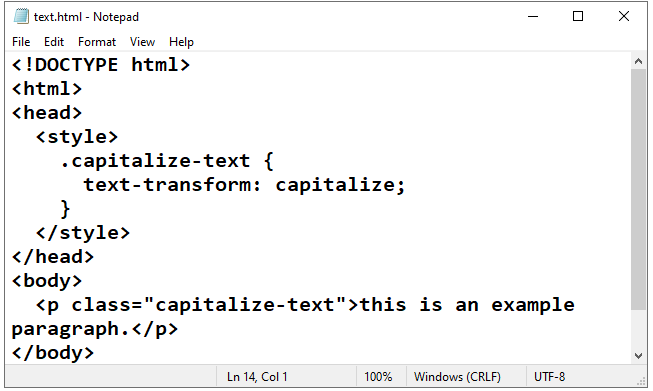
1)open notepad text Editor the create test.html by writing the the following code:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.capitalize-text {
text-transform: capitalize;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="capitalize-text">this is an example paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have a paragraph (<p>) element with the class name capitalize-text.
2-The CSS style defined within the <style> tags targets the elements with this class and applies the text-transform: capitalize; property to capitalize the first letter of each word.
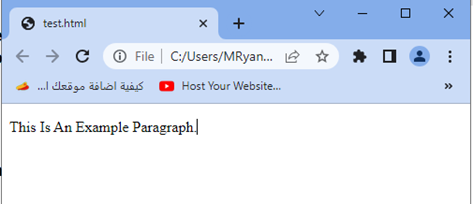
3-When you open this HTML file in a web browser, the paragraph text will be displayed as “This Is An Example Paragraph.”
Try to adjust the class name or apply the text-transform: capitalize; property to different HTML elements as needed.
Uppercase: complete code in html
Here’s an example of how you can use the text-transform: uppercase; property in HTML and CSS to convert text to uppercase:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.uppercase-text {
text-transform: uppercase;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="uppercase-text">this is an example paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have a paragraph (<p>) element with the class name uppercase-text.
2-The CSS style defined within the <style> tags targets the elements with this class and applies the text-transform: uppercase; property to convert the text to uppercase.
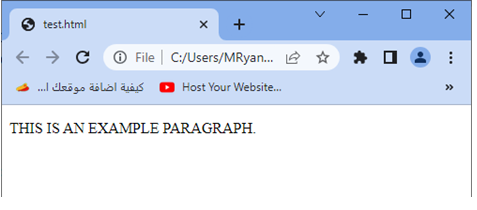
3-When you open this HTML file in a web browser, the paragraph text will be displayed as “THIS IS AN EXAMPLE PARAGRAPH.”
Try to adjust the class name or apply the text-transform: uppercase; property to different HTML elements as needed.
lowercase: complete code in html
Here’s an example of how you can use the text-transform: lowercase; property in HTML and CSS to convert text to lowercase:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.lowercase-text {
text-transform: lowercase;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="lowercase-text">THIS IS AN EXAMPLE PARAGRAPH.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have a paragraph (<p>) element with the class name lowercase-text.
2-The CSS style defined within the <style> tags targets the elements with this class and applies the text-transform: lowercase; property to convert the text to lowercase.
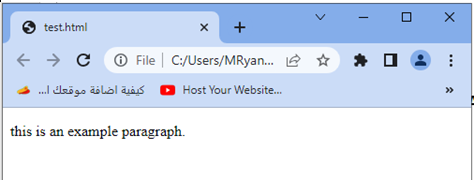
3-When you open this HTML file in a web browser, the paragraph text will be displayed as “this is an example paragraph.”
Try to adjust the class name or apply the text-transform: lowercase; property to different HTML elements as needed.
Initial: complete code in html
Here’s an example of how you can use the text-transform: initial; property in HTML and CSS to set the capitalization or case of text to its default value:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.initial-text {
text-transform: initial;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="initial-text">This is an example paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have a paragraph (<p>) element with the class name initial-text.
2-The CSS style defined within the <style> tags targets the elements with this class and applies the text-transform: initial; property to set the capitalization or case of the text to its default value.
When you open this HTML file in a web browser, the paragraph text will be displayed as “This is an example paragraph.” with the capitalization and case unaffected.
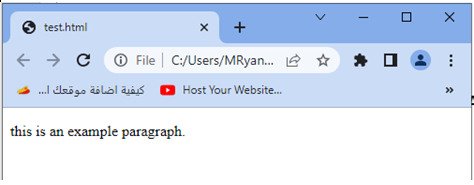
Try to adjust the class name or apply the text-transform: initial; property to different HTML elements as needed.
inherit: complete code in html
Here’s an example of how you can use the text-transform: inherit; property in HTML and CSS to inherit the capitalization or case from its parent element:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.parent {
text-transform: uppercase;
}
.child {
text-transform: inherit;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="parent">
<p class="child">This is an example paragraph.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have a <div> element with the class name parent, which has the text-transform: uppercase; property applied to it.
2-Inside this <div>, we have a paragraph (<p>) element with the class name child.
3-The CSS style defined for the .child class applies the text-transform: inherit; property, which means it will inherit the capitalization or case from its parent element.
When you open this HTML file in a web browser, the paragraph text will be displayed as “THIS IS AN EXAMPLE PARAGRAPH.” since it inherits the uppercase transformation from its parent <div>.
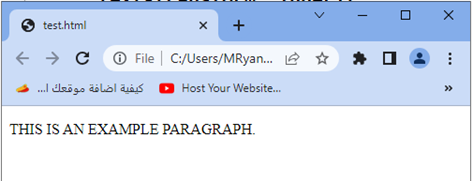
Try to adjust the class names or apply the text-transform: inherit; property to different HTML elements as needed.
Uses of css Text Transformation
The CSS text-transform property has various uses and can be beneficial in different scenarios. Here are some common use cases for the text-transform property:
Capitalizing or stylizing headings:
You can use text-transform to set the capitalization or case of headings (<h1>, <h2>, etc.) to match the desired style. For example, you can make all headings uppercase using text-transform: uppercase; to create a consistent and visually appealing design.
Capitalizing or stylizing headings: complete code in html
Here’s an example of how you can use the text-transform property in HTML and CSS to capitalize or stylize headings:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
h1 {
text-transform: uppercase;
}
h2 {
text-transform: capitalize;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is an example of an uppercase heading</h1>
<h2>this is an example of a capitalized heading</h2>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have an <h1> heading element that has the CSS style text-transform: uppercase; applied to it.
2-This will transform all the text within the <h1> element to uppercase.
2-Similarly, we have an <h2> heading element that has the CSS style text-transform: capitalize; applied to it.
3-This will capitalize the first letter of each word within the <h2> element.
When you open this HTML file in a web browser, you will see the <h1> heading displayed in uppercase and the <h2> heading with the first letter of each word capitalized.
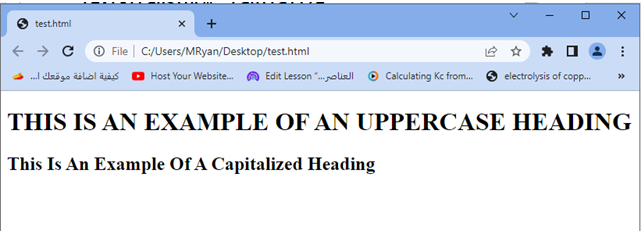
Try to adjust the styles, add more headings, or apply the text-transform property to other HTML elements as needed.
Formatting text inputs:
When dealing with user input in text fields or textareas, you may want to enforce specific capitalization rules. By applying text-transform to input fields or textarea elements, you can ensure that the user’s input is consistently transformed to uppercase or lowercase, depending on your requirements.
Formatting text inputs: complete code in html
Here’s an example of how you can use the text-transform property in HTML and CSS to format text inputs and enforce specific capitalization rules:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.uppercase-input {
text-transform: uppercase;
}
.lowercase-input {
text-transform: lowercase;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<label for="uppercase">Uppercase Input:</label>
<input type="text" id="uppercase" class="uppercase-input">
<label for="lowercase">Lowercase Input:</label>
<input type="text" id="lowercase" class="lowercase-input">
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have two text input fields.
2-The first input field has the class uppercase-input, and the second input field has the class lowercase-input.
3-The CSS styles defined within the <style> tags target these classes and apply the text-transform property accordingly.
4-The uppercase-input class applies text-transform: uppercase;, which means any text entered into that input field will be automatically converted to uppercase.
5-Similarly, the lowercase-input class applies text-transform: lowercase;, which converts any entered text to lowercase.
When you open this HTML file in a web browser, you will see two text input fields. Any text you type into the “Uppercase Input” field will automatically be converted to uppercase, while any text you type into the “Lowercase Input” field will be converted to lowercase.
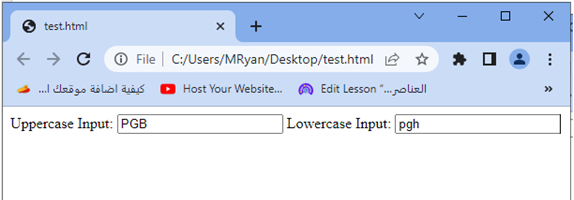
Try to adjust the class names, add more input fields, or apply the text-transform property to different HTML elements as needed.
Styling navigation menus:
text-transform can be used to style navigation menus by converting the text to uppercase or capitalizing the first letter of each word. This can help create a uniform and visually appealing navigation experience.
Styling navigation menus: complete code in html
Here’s an example of how you can use the text-transform property in HTML and CSS to style navigation menus:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.nav-menu {
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.nav-menu li {
display: inline-block;
margin-right: 10px;
}
.nav-menu li a {
text-transform: uppercase;
text-decoration: none;
color: #333;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul class="nav-menu">
<li><a href="#">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#">About</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Services</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Contact</a></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have a navigation menu represented by an unordered list (<ul>) with the class nav-menu.
2-Each menu item is represented by a list item (<li>) element. 3-The CSS styles defined within the <style> tags target these elements to style the navigation menu.
4-The .nav-menu class sets the list style to none, removes padding and margin, providing a clean and consistent layout for the menu.
5-The .nav-menu li selector styles each list item to display inline and adds some spacing between them using the margin-right property.
6-The .nav-menu li a selector styles the anchor (<a>) elements within each list item. In this example, text-transform: uppercase; is applied to convert the text to uppercase.
7-Additional styles such as removing the underline with text-decoration: none;, setting the text color to #333, and applying a bold font weight are also included.
When you open this HTML file in a web browser, you will see a navigation menu displayed as a horizontal list, with each menu item styled as uppercase.
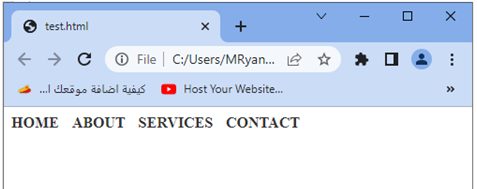
Try to modify the class names, add more menu items, or apply additional styles to further customize your navigation menu.
Adjusting text appearance in specific sections:
By selectively applying text-transform to specific elements or sections of your HTML document, you can modify the capitalization or case to suit your design needs. This allows you to highlight or differentiate certain text content within your webpage.
Here’s an example of how you can use the text-transform property in HTML and CSS to adjust the text appearance in specific sections:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.section-heading {
text-transform: uppercase;
color: blue;
}
.section-content {
text-transform: lowercase;
font-style: italic;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="section">
<h2 class="section-heading">This is the Heading</h2>
<p class="section-content">This is the content of the section.</p>
</div>
<div class="section">
<h2 class="section-heading">Another Heading</h2>
<p class="section-content">More content in this section.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have two sections represented by <div> elements with the class name section.
2-Each section consists of a heading (<h2>) element with the class name section-heading and a paragraph (<p>) element with the class name section-content.
3-The CSS styles defined within the <style> tags target these classes to adjust the text appearance.
4-The .section-heading class sets the text-transform property to uppercase to convert the text of the section headings to uppercase. Additionally, it sets the text color to blue.
5-The .section-content class sets the text-transform property to lowercase to convert the text of the section content to lowercase. It also sets the font style to italic.
When you open this HTML file in a web browser, you will see two sections displayed, with the headings styled as uppercase and blue, and the content styled as lowercase and italicized.
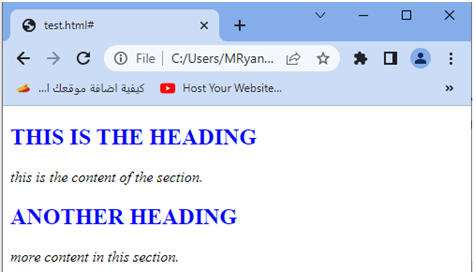
Try to modify the class names, add more sections, or apply additional styles to further adjust the text appearance in different sections of your HTML document.
Adjusting text appearance in specific sections: complete code in html
Here’s an updated example of how you can use the text-transform property in HTML and CSS to adjust the text appearance in specific sections:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.uppercase-section {
text-transform: uppercase;
color: red;
}
.lowercase-section {
text-transform: lowercase;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="uppercase-section">
<h2>This is an Uppercase Section</h2>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.</p>
</div>
<div class="lowercase-section">
<h2>This is a Lowercase Section</h2>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have two sections represented by <div> elements.
2-The first section has the class uppercase-section, and the second section has the class lowercase-section.
3-The CSS styles defined within the <style> tags target these classes to adjust the text appearance.
4-The .uppercase-section class sets the text-transform property to uppercase to convert the text of the section to uppercase. Additionally, it sets the text color to red.
5-The .lowercase-section class sets the text-transform property to lowercase to convert the text of the section to lowercase. It also sets the font weight to bold.
When you open this HTML file in a web browser, you will see two sections displayed. The text in the first section will be in uppercase and red, while the text in the second section will be in lowercase and bold.
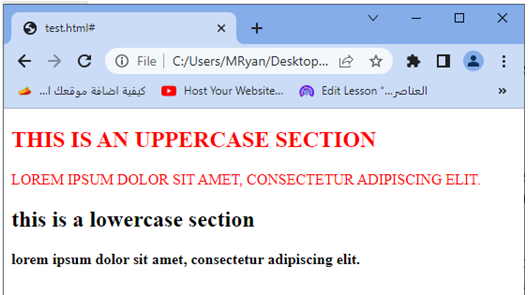
Try to modify the class names, add more sections, or apply additional styles to further adjust the text appearance in different sections of your HTML document.
Language-specific styling:
Some languages or writing systems have specific capitalization rules. By utilizing text-transform, you can ensure the correct capitalization or case for text in different languages, improving readability and adhering to cultural or linguistic norms.
Language-specific styling: complete code in html
Here’s an example of how you can use the text-transform property in HTML and CSS to apply language-specific styling:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.japanese-text {
text-transform: uppercase;
font-family: "Hiragana";
}
.german-text {
text-transform: lowercase;
font-family: "Arial";
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="japanese-text">
<h2>This is Japanese Text</h2>
<p>こんにちは、世界!</p>
</div>
<div class="german-text">
<h2>This is German Text</h2>
<p>Hallo Welt!</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have two sections represented by <div> elements.
2-The first section has the class japanese-text, and the second section has the class german-text. The CSS styles defined within the <style> tags target these classes to apply language-specific styling.
3-The .japanese-text class sets the text-transform property to uppercase to convert the Japanese text to uppercase. It also specifies the font family as “Hiragana” to ensure the text is displayed correctly.
4-The .german-text class sets the text-transform property to lowercase to convert the German text to lowercase. It specifies the font family as “Arial” for consistent display.
When you open this HTML file in a web browser, you will see two sections displayed. The Japanese text in the first section will be converted to uppercase and displayed with the specified font family, while the German text in the second section will be converted to lowercase and displayed with the specified font family.
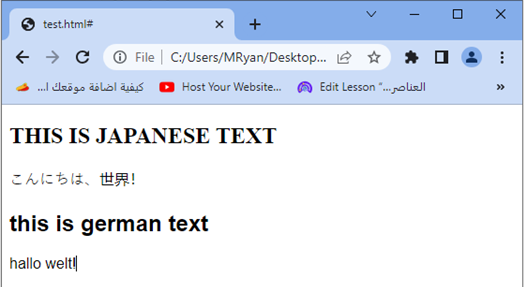
Note that the font family and text transformation rules used in this example are for illustration purposes. You should replace them with appropriate font families and text transformations based on the languages you are working with.
Try to modify the class names, add more sections with different languages, or apply additional styles to further customize the language-specific styling of your HTML document.
These are just a few examples of how the text-transform property can be used in CSS. It offers flexibility and control over the appearance of text, allowing you to customize and enhance the visual presentation of your web content.
simple application about this lesson
Here’s a simple application that demonstrates the use of CSS text-transform property:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
.uppercase-heading {
text-transform: uppercase;
}
.lowercase-content {
text-transform: lowercase;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="uppercase-heading">Welcome to My Website</h1>
<div class="lowercase-content">
<h2>About Me</h2>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Sed nec nulla non tortor feugiat varius.</p>
</div>
<div class="lowercase-content">
<h2>Contact Information</h2>
<p>Email: info@example.com</p>
<p>Phone: 123-456-7890</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In this example, we have a simple webpage with three sections.
2-The heading “Welcome to My Website” is styled using the .uppercase-heading class, which applies text-transform: uppercase;.
3-This makes the heading appear in uppercase letters.
4-The content sections, on the other hand, are styled using the .lowercase-content class, which applies text-transform: lowercase;. This transforms the text in these sections to lowercase.
When you open this HTML file in a web browser, you will see the heading “Welcome to My Website” displayed in uppercase, while the content sections with headings “About Me” and “Contact Information” are displayed in lowercase.
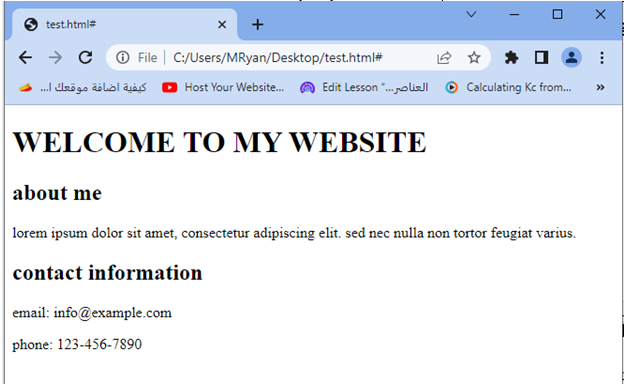
Try to modify the content, add more sections, or apply different styles to further explore the possibilities of the text-transform property.
Quiz with answers
Here’s a multiple-choice quiz about the CSS text-transform property:
1-Which CSS property is used to transform the text appearance?
a) text-style
b) text-transform
c) text-decoration
d) text-format
2-What is the purpose of the text-transform property?
a) Adjust the spacing between characters
b) Change the font size of the text
c) Modify the text appearance
d) Control the text alignment
3-How can you convert all text to uppercase using CSS?
a) text-transform: uppercase;
b) text-transform: lowercase;
c) text-transform: capitalize;
d) text-transform: inherit;
4-Which value of the text-transform property converts the first letter of each word to uppercase?
a) uppercase
b) lowercase
c) capitalize
d) inherit
5-True or False: The text-transform property only affects the visual representation of the text and does not change the actual content.
a) True
b) False
Answers:
- b) text-transform
- c) Modify the text appearance
- a) text-transform: uppercase;
- c) capitalize
- a) True
6-Which value of the text-transform property converts all text to lowercase?
a) uppercase
b) lowercase
c) capitalize
d) none
7-What is the purpose of the capitalize value in the text-transform property?
a) Converts all text to uppercase
b) Converts all text to lowercase
c) Converts the first letter of each word to uppercase
d) Removes any text transformation
8-Which of the following CSS properties can be used to adjust the appearance of headings?
a) text-align
b) text-transform
c) text-decoration
d) font-family
9-When applying the text-transform property to a specific HTML element, what happens to the text within that element?
a) The text is transformed visually but not in the source code.
b) The text is transformed both visually and in the source code.
c) The text is transformed in the source code but not visually.
d) The text remains unchanged.
10-True or False: The text-transform property is only applicable to text within headings (e.g., <h1>, <h2>, etc.).
a) True
b) False
Answers:
- b) lowercase
- c) Converts the first letter of each word to uppercase
- b) text-transform
- a) The text is transformed visually but not in the source code.
- b) False
Feel free to continue using this quiz to further test your understanding of the CSS text-transform property.
11-Which of the following values of the text-transform property converts all characters to their initial capital letter?
a) uppercase
b) lowercase
c) capitalize
d) initial
12-How can you apply the text-transform property to only the first letter of each word within a paragraph?
a) Use the text-transform property with the value capitalize.
b) Wrap the first letter of each word in a <span> element and style it with CSS.
c) Apply the text-transform property to the <p> element directly.
d) Use JavaScript to manipulate the text.
13-Which CSS property can be used to remove any text transformation applied to an element?
a) text-decoration
b) text-transform
c) text-align
d) text-indent
14-True or False: The text-transform property affects the text in all descendant elements.
a) True
b) False
15-What is the default value of the text-transform property?
a) uppercase
b) lowercase
c) capitalize
d) none
Answers:
- c) capitalize
- b) Wrap the first letter of each word in a <span> element and style it with CSS.
- b) text-transform
- b) False
- d) none
16-Which CSS property is used to set the spacing between characters?
a) letter-spacing
b) text-spacing
c) word-spacing
d) character-spacing
17-How can you apply the text-transform property to all text within an HTML document?
a) Apply it to the <body> element.
b) Apply it to the <html> element.
c) Apply it to the <head> element.
d) Apply it to each individual text element.
18-Which value of the text-transform property displays the text exactly as it is, without any transformation?
a) none
b) normal
c) transform-none
d) default
19-What is the purpose of the text-transform property in the context of accessibility?
a) It improves the legibility of the text.
b) It makes the text more visually appealing.
c) It ensures compatibility with screen readers and assistive technologies.
d) It prevents users from selecting and copying the text.
20-True or False: The text-transform property can be animated using CSS transitions or animations.
a) True
b) False
Answers:
- a) letter-spacing
- a) Apply it to the <body> element.
- a) none
- c) It ensures compatibility with screen readers and assistive technologies.
- a) True
Feel free to continue using this quiz to further test your understanding of the CSS text-transform property.
21-Which of the following values of the text-transform property transforms the text appearance in a way that each word starts with an uppercase letter and the remaining letters are lowercase?
a) uppercase
b) lowercase
c) capitalize
d) initial
22-What happens when the text-transform property is applied to an inline element, such as <span>?
a) The property has no effect on inline elements.
b) The text within the inline element is transformed.
c) The inline element is converted to a block-level element.
d) The property throws an error because it cannot be applied to inline elements.
23-Which CSS property can be used to adjust the appearance of links when the text-transform property is applied?
a) text-decoration
b) text-transform
c) color
d) font-weight
24-True or False: The text-transform property affects the text wrapping behavior within an element.
a) True
b) False
25-What is the purpose of using the text-transform property instead of changing the text directly in HTML?
a) It provides better performance.
b) It allows for easier maintenance and flexibility.
c) It has better compatibility with older browsers.
d) It reduces the file size of the HTML document.
Answers:
- c) capitalize
- b) The text within the inline element is transformed.
- a) text-decoration
- b) False
- b) It allows for easier maintenance and flexibility.
Try to continue using this quiz to further test your understanding of the CSS text-transform property.
