Introduction to CSS: A Comprehensive Guide | Tutorial, Examples, and Best Practices
Introduction to CSS: A Comprehensive Guide | Tutorial, Examples, and Best Practices
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a stylesheet language used to describe the presentation and layout of a web page written in HTML (Hypertext Markup Language).
It is a fundamental technology in web development that allows developers to control the visual appearance of a website.
CSS works by selecting HTML elements and applying various styles and properties to them. These styles define how elements should be displayed, such as their colors, fonts, sizes, spacing, positioning, and more. By separating the presentation layer (CSS) from the content layer (HTML), developers can make changes to the design of a website without altering the underlying HTML structure.
Importance and uses of CSS
CSS plays a vital role in web development and offers several benefits and uses.
Here are some of the key importance and uses of CSS:
Separation of Concerns:
CSS allows for the separation of the presentation layer (styles and layout) from the content layer (HTML structure).
This separation makes it easier to maintain and update websites since changes to the design can be made independently of the content.
Consistent Styling:
CSS enables the application of consistent styles across a website.
By defining styles in a central CSS file, you can ensure that elements with the same class or tag have a unified appearance, providing a cohesive and professional look to the entire site.
Flexibility and Control:
CSS provides fine-grained control over the visual presentation of web pages. You can modify various aspects, including colors, fonts, sizes, spacing, backgrounds, borders, and more. With CSS, you can achieve complex layouts and implement specific design requirements.
Reusability:
CSS supports the concept of reusable styles. You can define styles once and apply them to multiple elements throughout a website. This reusability not only saves development time but also helps maintain consistency and reduces the size of HTML documents.
Easy Maintenance and Updates:
By externalizing styles into separate CSS files, we can make changes or updates to the design without modifying the underlying HTML structure.
This modularity simplifies maintenance and allows for easier collaboration between developers and designers.
Responsive Design:
CSS is important for creating responsive websites that adapt to different screen sizes and devices. Media queries enable you to apply specific styles based on the characteristics of the user’s device, ensuring optimal viewing experiences on desktops, tablets, and mobile devices.
Browser Compatibility:
CSS is widely supported by modern web browsers, making it a reliable and consistent solution for web development. Browser vendors strive to adhere to CSS standards, ensuring that websites styled with CSS display correctly across different platforms and devices.
Accessibility:
CSS helps improve the accessibility of web content. By using CSS to control the presentation, developers can separate structural elements from visual styling, making it easier for assistive technologies like screen readers to interpret and convey the content to users with disabilities.
Print Styling:
CSS provides the ability to create print-friendly versions of web pages. By applying specific print styles, you can optimize the layout and formatting for printing, ensuring that important content is presented legibly on paper.
Overall, CSS is essential for creating visually appealing, responsive, and maintainable websites. It empowers developers to control the presentation layer, achieve consistent designs, and enhance user experience across different devices and browsers.
Requirement to write CSS
To write CSS, you need the following requirements:
1-Text Editor or Integrated Development Environment (IDE):
You’ll need a text editor or IDE to write and edit your CSS code.
There are many options available, such as Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, Atom, or Notepad++. Choose a text editor that suits your preferences and provides features like syntax highlighting and code formatting for CSS.
Here to download
-HTML Structure: CSS is used to style and format HTML elements. Therefore, you should have an understanding of HTML and have the HTML structure in place before you start writing CSS. You can create an HTML file using a text editor and define the structure of your web page using HTML tags.
2-CSS Syntax:
Familiarize yourself with the syntax and rules of CSS.
CSS uses a selector-based syntax to target HTML elements and apply styles to them.
3-Web Browser:
To test and see the results of your CSS styles, you need a web browser. Modern web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge are commonly used for web development and have built-in developer tools that allow you to inspect and debug your CSS.
Here to download them:
Safari: (pre-installed on macOS)
These tools can be downloaded from their respective official websites. Simply visit the links provided and follow the instructions to download and install them on your computer.
Remember to save your CSS file with a .css extension and link it properly to your HTML file for the styles to take effect.
With these requirements in place, you can start writing CSS to style and enhance the appearance of your web pages.
It’s worth noting that most text editors and web browsers are available for multiple operating systems, so make sure to select the appropriate version based on your operating system (Windows, macOS, or Linux).
step by step how to write CSS code
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write CSS code:
Step 1: create HTML file
– Open your preferred text editor and create a new HTML file.
– Use HTML tags to define the structure and content of your page.
– Save the file with a (test.html) extension.
Step 2: Create a CSS File
then create a new CSS file in the same directory as your HTML file.
-Open your text editor and create a new file.
-Save the file with a .css extension.
For example, you can name it “styles.css”.
Step 3: Link the CSS File to HTML
In the head section of your HTML file, add a link to your CSS file.
Use the <link> tag with the “rel” attribute set to “stylesheet” and the “href” attribute pointing to the location of your CSS file.
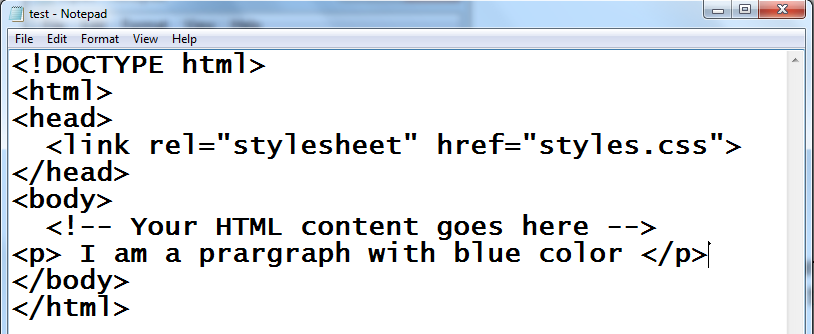
For example:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css"> </head> <body> <!-- Your HTML content goes here --> </body> </html>
Step 4: Target HTML Elements with CSS Selectors
In your CSS file, you can start writing CSS code to target and style specific HTML elements. CSS selectors allow you to select elements based on their tag names, classes, IDs, attributes, and more.
For example, to target all paragraphs and change their color to blue, you can use the following CSS code:
p {
color: blue;
}
Step 5: Define CSS Properties and Values
Once you’ve targeted an HTML element, you can define CSS properties and their corresponding values to style the element. CSS properties control various aspects of an element, such as colors, fonts, sizes, spacing, and more.
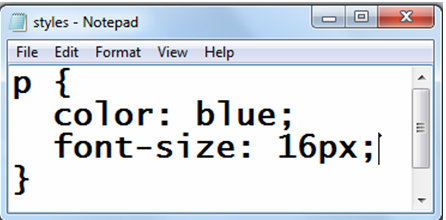
For example, to change the font size of all paragraphs to 16 pixels, you can add the following CSS code:
p {
color: blue;
font-size: 16px;
}
Step 6: Save and Refresh the Web Page
Save your HTML and CSS files.
Open the HTML file in your web browser, and you should see the changes made by your CSS styles.
If the changes don’t appear, double-check that the CSS file is correctly linked in the HTML file.
Remember to save your CSS file each time you make changes and refresh the web page to see the updated styles.
complete code example
Here’s a complete code example that demonstrates the process of writing CSS code:
1-HTML file (index.html):
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css"> </head> <body> <h1>Welcome to My Website</h1> <p>This is a paragraph.</p> <p class="highlight">This is another paragraph with a class.</p> </body> </html>
2- CSS (styles.css):
/* Target all paragraphs */
p {
color: red;
font-size: 24px;
}
/* Target the paragraph with the "highlight" class */
p.highlight {
background-color: yellow;
font-weight: bold;
}

Open the page with browser to see:
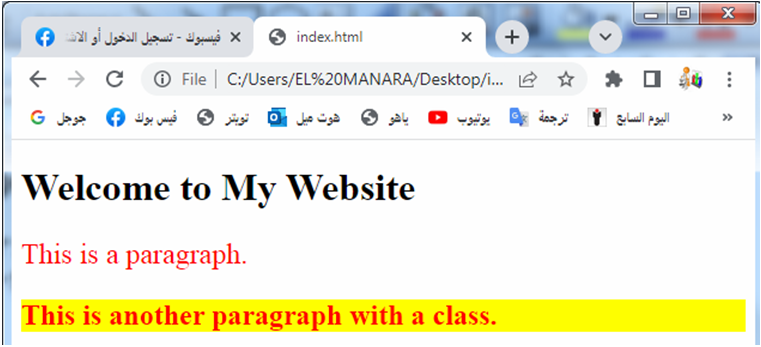
Explanation:
we create 2 files :
1-The HTML file contains a simple structure with an <h1> heading and two paragraphs (<p>).
2-The CSS file is linked to the HTML file using the <link> tag in the head section.
3-In the CSS file, the first CSS rule targets all paragraphs (p) and sets their color to red and font size to 16 pixels.
4-The second CSS rule targets the paragraph with the class “highlight” (p.highlight) and sets its background color to yellow and font weight to bold.
When you open the HTML file in a web browser, the paragraphs will be styled according to the CSS rules.
5-The first paragraph will have red text with a font size of 16 pixels, while the second paragraph with the “highlight” class will have a yellow background and bold text.
You can add more HTML elements and write additional CSS code to style them as desired. Remember to save both the HTML and CSS files in the same directory and refresh the web page in the browser to see the changes.
Quiz with answers about this lesson
Here’s a multiple-choice quiz with answers based on the lesson about CSS:
1-What does CSS stand for?
a) Cascading Style Sheets
b) Central Style Syntax
c) Creative Styling System
d) Code Styling Solutions
Answer: a) Cascading Style Sheets
2-Which of the following is NOT a use of CSS?
a) Separation of concerns
b) Flexibility and control over styling
c) Managing server-side operations
d) Consistent styling across a website
Answer: c) Managing server-side operations
3-How is CSS typically written in a web project?
a) In a separate CSS file with a .css extension
b) Within the HTML file using the <style> tag
c) Inline within HTML elements using the style attribute
d) All of the above
Answer: d) All of the above
4-Which of the following is used to select HTML elements in CSS?
a) ID selectors
b) Class selectors
c) Element selectors
d) All of the above
Answer: d) All of the above
5-What is the purpose of the CSS box model?
a) To define the structure of an HTML page
b) To control the layout and spacing of elements
c) To specify the color scheme of a website
d) To handle user interactions and events
Answer: b) To control the layout and spacing of elements
6-How can CSS be used to create a responsive website?
a) By using media queries to apply different styles based on screen size
b) By using JavaScript to dynamically adjust the styles
c) By creating separate CSS files for different devices
d) By using CSS preprocessors like SASS or LESS
Answer: a) By using media queries to apply different styles based on screen size
7-True or False: CSS is only supported by certain web browsers.
Answer: False. CSS is widely supported by modern web browsers.
8-What does the “C” in CSS stand for?
a) Creative
b) Cascading
c) Centralized
d) Coordinated
Answer: b) Cascading
9-Which section of an HTML file is used to link an external CSS file?
a) <head>
b) <body>
c) <footer>
d) <style>
Answer: a) <head>
10-How does CSS contribute to web accessibility?
a) By allowing developers to define semantic HTML structure
b) By separating the presentation layer from the content
c) By enabling the use of ARIA attributes for accessibility
d) All of the above
Answer: b) By separating the presentation layer from the content
11-Which of the following is NOT a valid CSS selector?
a) #myElement
b) .myClass
c) $myElement
d) p
Answer: c) $myElement
12-How can you apply multiple CSS classes to an HTML element?
a) Separate the classes with a comma (,)
b) Separate the classes with a plus sign (+)
c) Separate the classes with a space ( )
d) Separate the classes with a hyphen (-)
Answer: c) Separate the classes with a space ( )
13-Which CSS property is used to control the spacing between lines of text?
a) margin
b) padding
c) line-height
d) letter-spacing
Answer: c) line-height
14-What is the purpose of the CSS property “display: none;”?
a) It removes the element from the document flow and hides it completely.
b) It sets the element’s background color to none.
c) It displays the element as an inline block.
d) It applies a shadow effect to the element.
Answer: a) It removes the element from the document flow and hides it completely.
15-Which CSS property is used to create rounded corners on an element?
a) border-radius
b) border-style
c) border-color
d) border-width
Answer: a) border-radius
16-What is the CSS property used to change the color of text?
a) text-color
b) font-color
c) color
d) text-style
Answer: c) color
17-How can you include comments in CSS code?
a) /* This is a comment /
b) <!– This is a comment –>
c) // This is a comment //
d) # This is a comment #
Answer: a) / This is a comment */
18-Which CSS property is used to control the positioning of an element?
a) position
b) display
c) float
d) clear
Answer: a) position
19-Which CSS property is used to add shadows to elements?
a) shadow-effect
b) box-shadow
c) text-shadow
d) shadow-color
Answer: b) box-shadow
20-How can you include an external font in your CSS?
a) Use the @font-face rule
b) Use the font-style property
c) Use the font-family property
d) Use the import rule
Answer: a) Use the @font-face rule
