HTML Introduction
HTML Introduction
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is a markup language used to create and structure content for the World Wide Web. It was first introduced in 1993 by Tim Berners-Lee, a British computer scientist who is credited with inventing the World Wide Web.
HTML uses a set of tags to define the structure and content of a web page. Tags are enclosed in angle brackets <>, and usually come in pairs (e.g. <p> for opening paragraph tag, and </p> for closing paragraph tag). The content of a web page is typically divided into sections, with each section using a specific set of tags to define its content.
HTML documents can be viewed in web browsers, which interpret the tags and render the content accordingly. HTML also supports the use of styles and formatting to control the visual appearance of the content.
HTML has gone through several versions, with the latest being HTML5. HTML5 introduced new features such as improved multimedia support, better accessibility, and new semantic tags for structuring content.
importance and uses of html
HTML is an essential language for creating web pages and is used in conjunction with other languages such as CSS and JavaScript to build interactive and engaging web content. Some of the important uses and benefits of HTML are:
-
Creating web pages: HTML is the backbone of all web pages and is used to create the structure, layout, and content of a web page.
-
Cross-platform compatibility: HTML is supported by all major web browsers and can be used to create web pages that work seamlessly across different platforms, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and mobile devices.
-
Search engine optimization: HTML is used to create search engine-friendly web pages, which can help improve a website’s search engine ranking and visibility.
-
Accessibility: HTML allows web developers to create web pages that are accessible to people with disabilities, such as visually impaired users who rely on screen readers.
-
Multimedia support: HTML5 introduced new multimedia tags that allow web developers to add audio, video, and other interactive elements to web pages without relying on third-party plugins.
-
Mobile optimization: HTML can be used to create mobile-responsive web pages that automatically adjust their layout and content based on the device’s screen size and orientation.
Overall, HTML is a fundamental language that is used to create and structure the content of web pages, making it an essential skill for web developers and designers.
what are the requirements to write HTML codes?
To write HTML code, you don’t need any special equipment or software. All you need is a text editor, which is a program that allows you to create and edit plain text files.
Most computers come with a built-in text editor, such as Notepad on Windows or TextEdit on macOS. These basic text editors can be used to write HTML code, but they don’t provide any syntax highlighting or other features specifically designed for web development.
There are also specialized text editors and integrated development environments (IDEs) that are designed for web development, such as Sublime Text, Atom, and Visual Studio Code. These tools often provide features like syntax highlighting, code completion, and debugging, which can make writing HTML code faster and easier.
In addition to a text editor, you’ll also need a web browser to view and test your HTML code. Most modern web browsers, such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Microsoft Edge, include developer tools that allow you to inspect and debug your HTML code directly within the browser.
Finally, it’s important to have a basic understanding of HTML syntax and structure in order to write effective code. There are many online resources and tutorials available that can help you learn HTML, including documentation from the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) and interactive online courses.
where are the integrated development environments (IDEs) to write HTML?
There are many integrated development environments (IDEs) available for writing HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code. Some of the most popular ones are:
-
Visual Studio Code: This is a free and open-source IDE developed by Microsoft. It has built-in support for HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, as well as a range of extensions that can be installed to add additional functionality.
-
Sublime Text: This is a lightweight and customizable text editor that supports HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It has a range of features designed for web development, such as syntax highlighting and code completion.
-
Atom: This is a free and open-source text editor developed by GitHub. It has built-in support for HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, as well as a range of plugins that can be installed to add additional functionality.
-
Brackets: This is a free and open-source text editor developed by Adobe. It has built-in support for HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, as well as a range of extensions that can be installed to add additional functionality.
-
WebStorm: This is a commercial IDE developed by JetBrains. It has built-in support for HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, as well as a range of features designed for web development, such as code completion, refactoring, and debugging.
These are just a few examples of the many IDEs available for writing HTML code. The choice of IDE depends on personal preference, project requirements, and other factors such as ease of use, performance, and features.
The links for each IDE editors:
Note that some of these IDEs have both free and paid versions, and some also offer free trials of their paid versions. It’s a good idea to try out a few different IDEs to see which one works best for your needs.
How to download The text Editors ?
To download an IDE, follow these general steps:
- Go to the website of the IDE you want to download.
- Look for a “Download” button or link on the website.
- Click the “Download” button or link to start the download process.
- Follow the instructions to download and install the IDE on your computer.
The specific steps may vary depending on the IDE and your operating system. Here are some additional details for the IDEs I mentioned earlier:
-
Visual Studio Code: To download Visual Studio Code, go to the website (https://code.visualstudio.com/) and click the “Download for [your operating system]” button. This will download an installer file, which you can run to install the IDE.
-
Sublime Text: To download Sublime Text, go to the website (https://www.sublimetext.com/) and click the “Download” button for your operating system. This will download a zip file, which you can extract and run to install the IDE.
-
Atom: To download Atom, go to the website (https://atom.io/) and click the “Download” button for your operating system. This will download an installer file, which you can run to install the IDE.
-
Brackets: To download Brackets, go to the website (http://brackets.io/) and click the “Download Brackets” button for your operating system. This will download an installer file, which you can run to install the IDE.
-
WebStorm: To download WebStorm, go to the website (https://www.jetbrains.com/webstorm/) and click the “Download” button for your operating system. This will download an installer file, which you can run to install the IDE.
Again, the specific steps may vary depending on your operating system and the IDE you choose. Be sure to read the instructions carefully and follow the prompts to complete the installation process.
What is about HTML Page Structure?
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is used to create the structure of a web page. A well-structured HTML page is important for both search engines and users to understand the content and layout of the page. Here’s a basic overview of the structure of an HTML page:
-
Document type declaration (DTD):
-
This is the first line of an HTML document that specifies the version of HTML being used. For example, the DTD for HTML5 is <!DOCTYPE html>.
-
HTML element: This is the root element of an HTML document, and it wraps all the other elements on the page. It is represented by the <html> tag.
-
Head element: This element contains meta information about the page that is not displayed in the main content area. It includes the page title, meta tags, links to stylesheets and scripts, and other data. It is represented by the <head> tag.
-
Body element: This element contains the main content of the page, such as text, images, videos, and other media. It is represented by the <body> tag.
-
Sections and subsections: The content of the <body> element is usually divided into sections and subsections, each with a specific purpose and heading. Section headings are typically marked up with the <h1> to <h6> tags, with <h1> being the most important and <h6> being the least important.
-
Content elements: These are the elements that make up the content of the page, such as text, images, videos, and other media. Examples include the <p> tag for paragraphs, the <img> tag for images, and the <video> tag for videos.
-
Semantic elements: HTML5 introduced a number of semantic elements that are used to provide more meaning and context to the content on a page. Examples include the <header> tag for the page header, the <nav> tag for navigation menus, and the <footer> tag for the page footer.
By following a well-defined HTML structure, you can create web pages that are easy to read, easy to maintain, and easy to understand for both humans and search engines.
How to create a simple HTML page ?
step by step how to use notepad to create HTML page ?
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use Notepad (available on Windows) to create an HTML page:
1-Open Notepad: Go to your computer’s Start menu, search for “Notepad,” and click on the Notepad application to open it.
2-Start a New Document: In Notepad, click on “File” in the top menu and then select “New” to start a new blank document.
3-Write HTML Code: In the empty Notepad document, you can start writing your HTML code. For example, you can begin with the basic structure of an HTML document:
4-Save the File: To save the file, click on “File” in the top menu, then select “Save As.” Choose a location on your computer where you want to save the HTML file. In the “Save as type” dropdown, select “All Files (.)” and name the file with a .html extension (e.g., “my-page.html”). Click “Save” to save the file.
5-View the HTML Page: After saving the HTML file, you can open it in a web browser to view the rendered page. Locate the saved HTML file on your computer, right-click on it, and select “Open With.” Choose your preferred web browser (e.g., Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox) to open the file. The browser will display the HTML page.
Note:
By following these steps, you can use Notepad to create an HTML page and view it in a web browser. Notepad is a simple text editor, so it doesn’t have advanced features like syntax highlighting or code completion, but it is sufficient for basic HTML coding.
For a more feature-rich coding experience, you might consider using specialized text editors like Visual Studio Code or Sublime Text, as mentioned earlier.
Follow the following steps:
1-Click on in taskbar

2-write :notepad on the search box
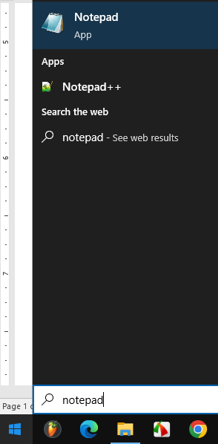
3-chose :Click notepad
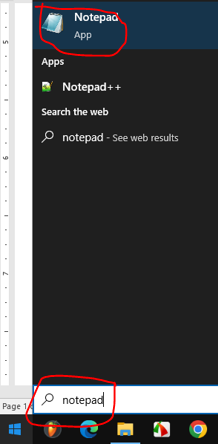
The window of notepad appears as :

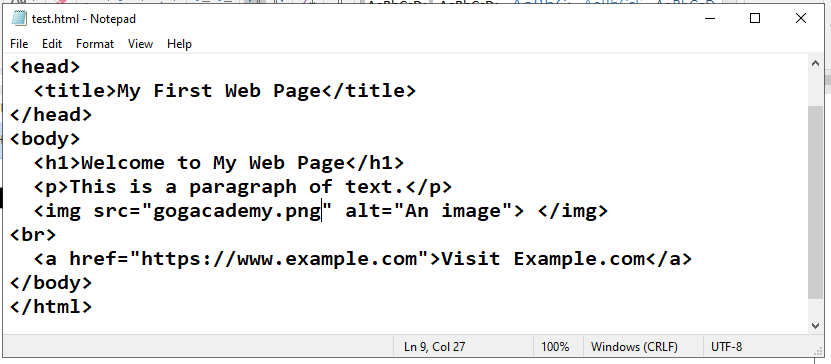
4-Write the following code in the nodepad
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>My First Web Page</title> </head> <body> <h1>Welcome to My Web Page</h1> <p>This is a paragraph of text.</p> <img src="gogacademy.png" alt="An image"> </img> <br> <a href="https://www.example.com">Visit Example.com</a> </body> </html>
5-From File menu >> save
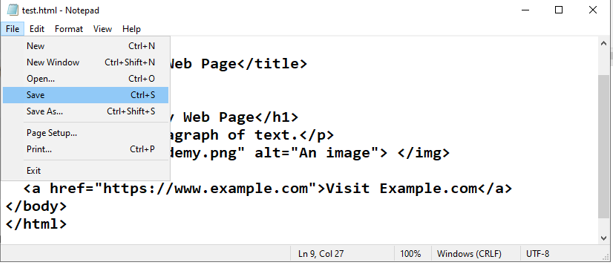
6-Then do the following:
Desktop >>> test.html > click Save
On desktop click on the page

The output:
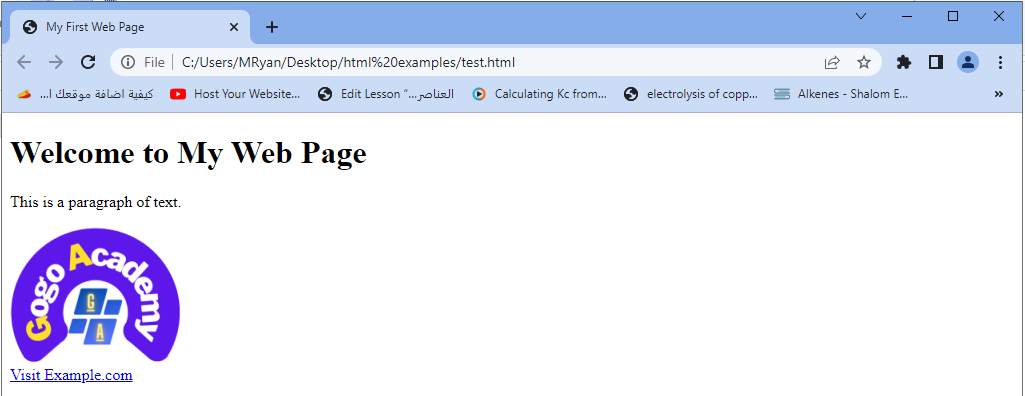
In the example above:
The <!DOCTYPE html> declaration specifies that the document is an HTML5 document.
The <html> element serves as the root element of the HTML document.
The <head> element contains metadata about the web page, such as the title displayed in the browser’s title bar.
The <body> element contains the visible content of the web page.
Inside the <body> element, we have various elements.
The <h1> element defines a heading, and the <p> element defines a paragraph.
The <img> element embeds an image into the page, and the <a> element creates a hyperlink to another web page.
