Properties of elements of the First transition elements
Properties of elements of the First transition elements
- atomic mass
- atomic radius ( volume)
- metalic properties
- density
- chemicla activity
- magnetic properties
- colors
-
catalytic activity
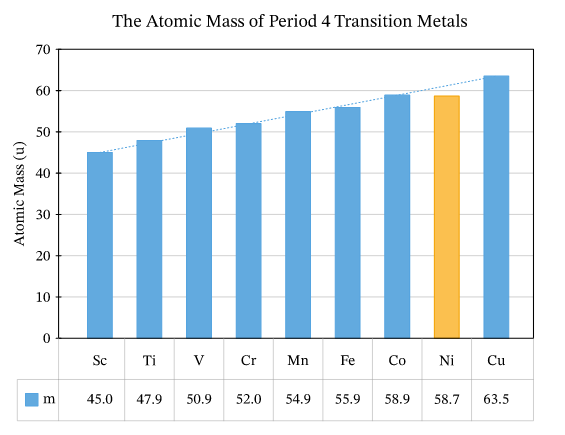
1)Atomic mass:
-
atomic mass increases as atomic number increase From (Sc) to (Cu)
- Except Nickel is abnormal GR?-because it has five stable isotopes with average mass 58.1 u.
2)Atomic size(radius): atomic radius constant
- -There is a little change in atomic radii as we move through first transition series
- – the atomic radius nearly constant from (Cr) to (Cu)

GR: The radii of transition elements are relatively constant?
-due to opposite factors:
1)by increasing atomic number the number of positive protons increases in nucleus so the effective nuclear charge increases so the nuclear attraction to electrons increases causing decrease the atomic radius
2)by increasing the number of electrons (-ve) in 3d-sublevel the repulsion force between electrons increases causing increasing the atomic radius
-Give Reason The transition elements are used in making alloys?
-because the atomic radii of these elements are relatively constant
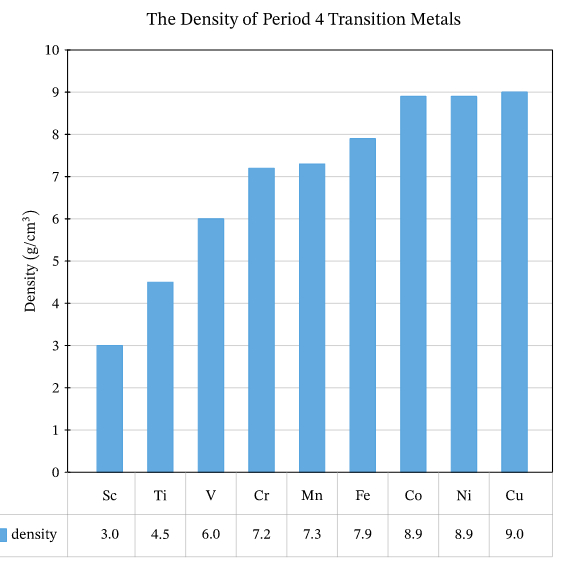
3)Density:
increases as atomic number increase GR?
-most of them have a high density which increases by increasing atomic number GR?
because their atomic mass increases while the atomic volume (size) is relatively constant

4)Metallic property:
ideal metals or ypical metals GR?
because:
1)solid, metallic luster, good conductor of heat
2)good conductor of electricity because they have free electrons to move conduct electricity
2)They have high density
2)have high melting and boiling point GR?
Because they have strong metallic bonds due to large numbers of valence electrons
5)Chemical activity:
increases from left to right where:
Sc21 Fe26 Cu29
a)scandium is very active GR? because it replaces Hydrogen of water vigorously
b)Iron is intermediate active so it form rust after months or years
c)copper is limited activity
Q: explain the chemical activity of 1s-tarnation elements?
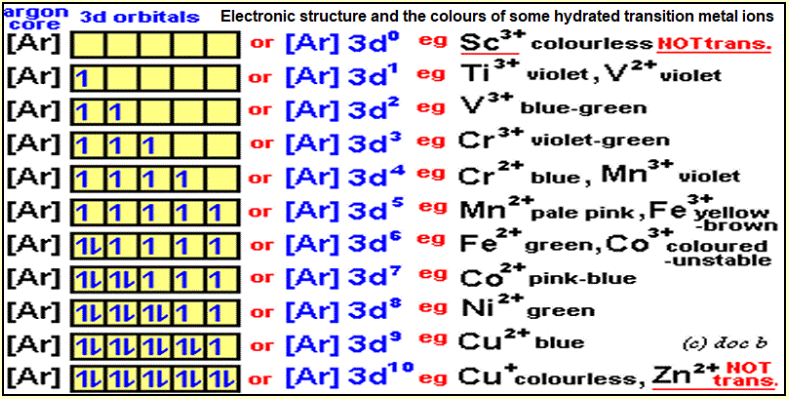
6)Magnetic property:
due to presence of unpaired electrons in ion, atom or molecules
– where the unpaired electrons spindle around itself causing small magnetic filled and attracted to external field
Diamagnetic: occurs when the sub-levels (orbitals)occupied by paired electrons so the paired
substances can be classified into:
|
1)para magnetic substance |
2) Diamagnetic substance |
| -Attracted to the magnet GR? due to unpaired electrons in (d) sub-level | -Repel to the magnet GR? due to absence of unpaired electrons in outer sub-level |
| -its ion has electronic configuration d1,d2….d9 | -it ‘s ion has electronic configuration ended by d0 or d10 |
|
As the number of unpaired electrons increases the magnetic attraction force increases and magnetic moment increases magnetic moment=number of single electrons |
-magnetic moment =ZERO |
-Magnetic moment =number of unpaired electrons
How to know the substance para or diamagnetic?
-You have elements have d1, d5 ,d6,d10 which is dia or paramagnetic and calculate magnetic moment
- There is no magnetic moment more than 5 GR?
- Q1-which of the following is paramagnetic or diamagnetic Fe2(SO4)3 – Zinc atom – iron(II)chloride- copper(II)ion-ZnSO4
We must calculate oxidation state to find the structure of d
How to calculate the oxidation state -arrange the following according(given:Cl=-1,O=-2,H=+1)
- ZnCl2 : Zn+(-1×2)=0 so Zn=+2 then Zn30:[Ar18]:4S2,3d10 Zn2+ :[Ar18]:4S0,3d10
so the single electrons in d-sub-level=5 electrons
its paramagenetic and the magnetic momentum=5
2-MnO2 Mn+2X-2=0 Mn=+4
Mn25:[Ar18]:4s2,d5 So Mn4+ :[Ar18]:4s0,d3
3-TiO2 : Ti22 Ti+2X-2=0 Ti=+4
Ti22 :[Ar18]:4s2,3d2 so Ti4+ :[Ar]:4s0,3d0
Q:Calculate the magnetic moment?TiO2 – Cr2O3 – CuCl2 -FeCl3
7-color property:
- –most transition elements compounds and their aqueous solution are colored
- The color appears when the substance absorbs some photons of the visible light so the remaining colors which are not absorbed by the substance (complementary color) is seen by the eye
- If it absorbs a certain color it appears by the complementary color
-The unpaired electrons absorb color and reflects another
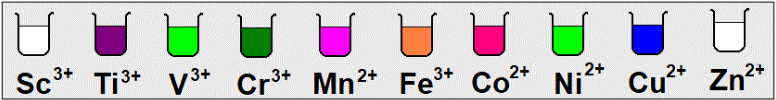
Give reasons:
1-most of ions of transition elements are colored?
-due to the single electrons in orbitals of(d1-9) sublevel that easily exited so it absorbs the color that has energy enough to excite it and appears by the complementary color
2-chromium III compounds appear green?
-because the energy of red color enough to excite the single electron of (Cr+++) so it absorbs red and appears by complementary color(green)
3-Sc+3 ,Cu+3,Zn+2 and ions of non-transition elements are colorless?
-Due to the empty sublevel (d0) as in Sc+3 or completely filled by electrons (d10) As in Cu+1 , Zn+2 and the energy needed to excite the paired electron is higher than that of visible light
3-V2O5 is yellow?
-because the unpaired electrons in d-sub-level absorbs energy = to violet and appears with complementary color to violet which is yellow
4-Glass is colorless?
-due to no single electrons in d-sublevel OR non-transition it needs energy not in the visible region
5-paper is white?-because it reflects all light falls on it mixing together form white
6-blackboard is black?-because it reflects non to eye and it absorbs all light fall on it
- Notes:
- 1-The substance appears colored if it contains single electrons in (d)
- 2-Colorless substance those ended by (d0-d10) or representative elements
- 3-par magnetic substance is colored
- 4- Diamagnetic substance is colorless
- 8-catalytic property: it related to unpaired electrons
-How catalyst works?
If we have reactants:
1-It makes temporary bonds with the reactants
2-which increases reactants concentration on the surface of catalyst
3-causing increase collision between reactants and changes the reactant molecules into activated molecules
4-That weaken bonds in reactants and forming new bonds in products that
5-That decreases activation energy in reaction and speed up the reaction
Example :decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen in presence of MnO2 as catalyst
