JavaScript Strings: Complete Guide to Working with Textual Data”
JavaScript Strings
Learn how to use JavaScript strings effectively. Understand string declaration, concatenation, length, character access, modification, and common methods. Improve your JavaScript string handling skills with practical examples.”
We will study the concepts of : JavaScript strings, working with strings, string declaration, string concatenation, string length, character access, string modification, string methods, JavaScript string examples
In JavaScript, a string is a sequence of characters enclosed in single quotes (”) or double quotes (“”). Strings are one of the primitive data types in JavaScript and are used to represent textual data.
Here’s an explanation of JavaScript strings and some examples of working with strings in JavaScript:
Declaration and Initialization of JavaScript string :
Strings can be declared and initialized by assigning a value to a variable using quotes.
Here’s an example:
let greeting = "Hello, World!";
JavaScript String Concatenation:
You can concatenate (join) two or more strings using the + operator.
Here’s an example:
let firstName = "Gogo"; let lastName = "Rabei"; let fullName = firstName + " " + lastName; // fullName will be "Gogo Rabei"
JavaSCript String Length:
You can find the length of a string using the length property. Here’s an example:
let message = "Hello!"; let length = message.length; // length will be 6
Accessing Characters:
Individual characters in a string can be accessed using square brackets and the index of the character. Note that string indices start from 0.
Here’s an example:
let text = "Hello"; let firstChar = text[0]; // firstChar will be "H"
Modifying Strings:
JavaScript strings are immutable, which means you cannot change an individual character in a string. However, you can create a new string by modifying the original string.
Here’s an example:
let greeting = "Hello!";
let newGreeting = greeting.replace("Hello", "Hi"); // newGreeting will be "Hi!"
JavaScript String Methods:
JavaScript provides various built-in methods to work with strings. Some commonly used methods include:
Here’s an example that demonstrates some of these concepts:
toUpperCase() and toLowerCase(): Convert a string to uppercase or lowercase.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Strings as Objects Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>JavaScript Strings as Objects Example</h1>
<script>
let name = "Gogo Rabei";
document.(name.toUpperCase()); // Output: " Gogo Rabei "
</script>
</body>
</html>
trim(): Remove whitespace from the beginning and end of a string.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Strings as Objects Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>JavaScript Strings as Objects Example</h1>
<script>
let name = " Gogo Rabei ";
document.write(name.trim()); // Output: " Gogo Rabei "
</script>
</body>
</html>
substring(startIndex, endIndex):
Extract a substring from a string based on the specified start and end indices.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Strings as Objects Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>JavaScript Strings as Objects Example</h1>
<script>
let name = "Mohammad";
document.write(name.substring(0,3)); // Output: "
substring(startIndex, endIndex)
</script>
</body>
</html>
The output: Moh
split(separator):
Split a string into an array of substrings based on a separator.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Strings as Objects Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>JavaScript Strings as Objects Example</h1>
<script>
let name = "Mohammad";
document.write(name.split(''));
</script>
</body>
</html>
The output:
M,o,h,a,m,m,a,d
These are just some basic operations and methods available for working with JavaScript strings. There are many more string-related functions and concepts that you can explore in the JavaScript documentation or further JavaScript learning resources.
Declaration and Initialization of String :complete code in html
To demonstrate the declaration and initialization of a JavaScript string in an HTML document, you can use the <script> tag within the HTML <body> section.
Here’s an example of complete HTML code that declares and initializes a string variable:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript String Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>JavaScript String Example</h1>
<script>
// Declaration and Initialization of a string
let message = "Hello, World!";
// Displaying the string by document.write()
alert(message);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, the <script> tag is used to enclose the JavaScript code.
2-Inside the script tags, we declare and initialize the string variable message with the value “Hello, World!”.
3-The console.log() statement is used to display the value of message in the browser’s console.
When you open this HTML file in a web browser and inspect the console, you should see the output “Hello, World!” printed in the console.

Note: The <script> tag can also be placed in the <head> section of the HTML document. However, it is generally recommended to place scripts at the end of the <body> section to ensure that the HTML content is loaded before executing the JavaScript code.
JavaScript String Concatenation: complete code in html
To demonstrate string concatenation in an HTML document using JavaScript, you can modify the previous HTML code. Here’s an example that concatenates two strings and displays the result:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>String Concatenation Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>String Concatenation Example</h1>
<script>
// String Concatenation
let firstName = "Gogo";
let lastName = "Rabei";
let fullName = firstName + " " + lastName;
// Displaying the concatenated string
document.write(fullName);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have added the JavaScript code inside the <script> tag.
2-We declare and initialize two string variables, firstName and lastName, with the values “Gogo” and “Rabei” respectively.
3-We then concatenate the two strings using the + operator and store the result in the fullName variable.
4-To display the concatenated string on the web page, we use the document.write() method. The document.write() method writes the specified content directly to the HTML document.
5-When you open this HTML file in a web browser, you should see the output “Gogo Rabei” displayed on the webpage.

JavaScript String Length:complete code in html
To demonstrate how to find the length of a string in an HTML document using JavaScript, you can modify the previous HTML code.
Here’s an example that calculates the length of a string and displays the result:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>String Length Example</title>
</head>
<body>
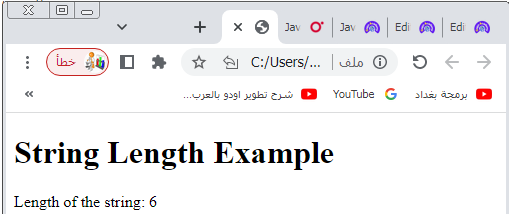
<h1>String Length Example</h1>
<script>
// String Length
let message = "Hello!";
let length = message.length;
// Displaying the length of the string
document.write("Length of the string: " + length);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have added the JavaScript code inside the <script> tag.
2-We declare and initialize a string variable message with the value “Hello!”.
3-We then use the length property of the string to find its length and store the result in the length variable.
4-To display the length of the string on the web page, we use the document.write() method.
5-The document.write() method writes the specified content directly to the HTML document.
6-When you open this HTML file in a web browser, you should see the output “Length of the string: 6” displayed on the webpage.
The number 6 represents the length of the string “Hello!”.
Accessing JavaScript string Characters: complete code in html
To demonstrate how to access individual characters in a string in an HTML document using JavaScript, you can modify the previous HTML code.
Here’s an example that accesses characters from a string and displays the result:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Accessing Characters Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Accessing Characters Example</h1>
<script>
// Accessing Characters
let text = "Hello";
let firstChar = text[0];
let lastChar = text[text.length - 1];
// Displaying the accessed characters
document.write("First character: " + firstChar + "<br>");
document.write("Last character: " + lastChar);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have added the JavaScript code inside the <script> tag.
2-We declare and initialize a string variable text with the value “Hello”.
3-We then access the first character of the string using text[0] and store it in the firstChar variable.
4-Similarly, we access the last character of the string using text[text.length – 1] and store it in the lastChar variable.
5-To display the accessed characters on the web page, we use the document.write() method.
6-The document.write() method writes the specified content directly to the HTML document.
7-We use <br> to create a line break between the displayed characters.
8-When you open this HTML file in a web browser, you should see the output:
First character: H
Last character: o
These lines represent the first and last characters of the string “Hello”.

Modifying Strings:complete code in html
To demonstrate how to modify strings in an HTML document using JavaScript, you can modify the previous HTML code.
Here’s an example that modifies a string and displays the result:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Modifying Strings Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Modifying Strings Example</h1>
<script>
// Modifying Strings
let greeting = "Hello!";
let newGreeting = greeting.replace("Hello", "Hi");
// Displaying the modified string
document.write("Modified string: " + newGreeting);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have added the JavaScript code inside the <script> tag.
2-We declare and initialize a string variable greeting with the value “Hello!”.
3-We then use the replace() method of the string to replace the word “Hello” with “Hi” in the greeting string.
4-The modified string is stored in the newGreeting variable.
5-To display the modified string on the web page, we use the document.write() method.
6-The document.write() method writes the specified content directly to the HTML document.
7-When you open this HTML file in a web browser, you should see the output “Modified string: Hi!” displayed on the webpage.
8-The original greeting “Hello!” is replaced with “Hi!” in the modified string.

Escape Character:complete code in html
To demonstrate the use of escape characters in an HTML document using JavaScript, you can modify the previous HTML code.
Here’s an example that utilizes an escape character and displays the result:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Escape Character Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Escape Character Example</h1>
<script>
// Escape Character
let message = "This is a \"quoted\" string.";
// Displaying the escaped string
document.write("Escaped string: " + message);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have added the JavaScript code inside the <script> tag.
2-We declare and initialize a string variable message with the value “This is a “quoted” string.”.
3-To include double quotes within the string, we use the escape character \ before each double quote.
4-To display the escaped string on the web page, we use the document.write() method.
5-The document.write() method writes the specified content directly to the HTML document.
6-When you open this HTML file in a web browser, you should see the output “Escaped string: This is a “quoted” string.” displayed on the webpage. The escape character \ allows the inclusion of double quotes within the string without terminating it prematurely.

Breaking Long Code Lines: complete code in html
To demonstrate breaking long lines of code in an HTML document using JavaScript, you can modify the previous HTML code.
Here’s an example that shows how to break long lines for improved readability:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Breaking Long Code Lines Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Breaking Long Code Lines Example</h1>
<script>
// Breaking Long Code Lines
let longString =
"This is a long string that needs to be broken " +
"into multiple lines for better readability.";
// Displaying the long string
document.write("Long string: " + longString);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have added the JavaScript code inside the <script> tag.
2-We have a long string that needs to be broken into multiple lines for better readability.
3-To break the line, we can use the + operator to concatenate multiple string literals.
4-Each line should end with a + sign followed by a space to indicate that the string continues to the next line.
5-To display the long string on the web page, we use the document.write() method. 6-The document.write() method writes the specified content directly to the HTML document.
When you open this HTML file in a web browser, you should see the output:

JavaScript Long string:
This is a long string that needs to be broken into multiple lines for better readability.
The long string is displayed correctly even though it is broken into multiple lines for improved readability.
JavaScript Strings as Objects: complete code in html
In JavaScript, strings can also be treated as objects.
Here’s an example that demonstrates using JavaScript strings as objects in an HTML document:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Strings as Objects Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>JavaScript Strings as Objects Example</h1>
<script>
// JavaScript Strings as Objects
let message = "Hello, World!";
let firstCharacter = message.charAt(0);
let substring = message.substring(7, 12);
let uppercase = message.toUpperCase();
// Displaying the results
document.write("First character: " + firstCharacter + "<br>");
document.write("Substring: " + substring + "<br>");
document.write("Uppercase: " + uppercase);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
1-In the above code, we have added the JavaScript code inside the <script> tag.
2-We have a string variable message initialized with the value “Hello, World!”.
3-We treat the message string as an object and use the following string methods:
- charAt(index): Returns the character at the specified index.
- Here, we use message.charAt(0) to get the first character.
- substring(startIndex, endIndex): Extracts a substring based on the specified start and end indices.
- Here, we use message.substring(7, 12) to get the substring “World”.
- toUpperCase(): Converts the string to uppercase.
- Here, we use message.toUpperCase() to convert the string to “HELLO, WORLD!”.
4-To display the results on the web page, we use the document.write() method.
5-The document.write() method writes the specified content directly to the HTML document.
6-We use <br> to create line breaks between the displayed results.
7-When you open this HTML file in a web browser, you should see the output:
First character: H
Substring: World
Uppercase: HELLO, WORLD!

These lines demonstrate the use of string methods as objects to perform operations on the string “Hello, World!”.
Quiz with answers
Here’s a multi-choice quiz with 25 questions based on the lesson about JavaScript strings. Each question is followed by four answer choices (A, B, C, and D), with the correct answer indicated in parentheses.
1-Which of the following is the correct way to declare a string variable in JavaScript?
- A) var message = “Hello”;
- B) let message = ‘Hello’;
- C) const message = “Hello”;
- D) All of the above (D)
2-What is the length of the string “Hello, World!”?
- A) 5
- B) 10
- C) 12
- D) 13 (D)
3-How can you access the second character of a string?
- A) str[0]
- B) str[1]
- C) str.charAt(1)
- D) All of the above (D)
4-Which method is used to convert a string to uppercase?
- A) toUpperCase()
- B) toLowercase()
- C) convertUppercase()
- D) None of the above (A)
5-What is the result of the string concatenation: “Hello” + ” ” + “World!”?
- A) “HelloWorld!”
- B) “Hello World!”
- C) “HelloWorld!”
- D) “HelloWorld” (B)
6-Which method is used to remove leading and trailing whitespace from a string?
- A) trim()
- B) removeWhitespace()
- C) clean()
- D) strip() (A)
7-How can you replace a specific part of a string with another value?
- A) replace()
- B) replaceString()
- C) change()
- D) modify() (A)
8-Which method splits a string into an array of substrings based on a separator?
- A) split()
- B) divide()
- C) explode()
- D) separate() (A)
9-What is the output of the following code: console.log(“Hello”.length);?
- A) 4
- B) 5
- C) 6
- D) 7 (B)
10-How do you escape a double quote within a string?
- A) ‘
- B) “
- C) \
- D) / (B)
11-Which method extracts a substring from a string?
- A) extract()
- B) getSubstring()
- C) substring()
- D) slice() (C)
12-What is the result of “Hello”.toUpperCase()?
- A) “hello”
- B) “HELLO”
- C) “Hello”
- D) “hELLO” (B)
13-How many characters are in an empty string?
- A) 0
- B) 1
- C) Undefined
- D) Error (A)
14-What does the following code snippet do? str.replace(“old”, “new”);
- A) Replaces all occurrences of “old” with “new” in the string str
- B) Replaces the first occurrence of “old” with “new” in the string str
- C) Replaces the last occurrence of “old” with “new” in the string str
- D) Does nothing, it’s an invalid syntax (B)
15-Which method is used to convert a string to lowercase?
- A) toUpperCase()
- B) toLowercase()
- C) convertLowercase()
- D) None of the above (B)
16-How can you find the last character of a string?
- A) str[length – 1]
- B) str.charAt(length)
- C) str.charAt(length – 1)
- D) All of the above (D)
17-What is the result of “Hello”.substring(1, 4)?
- A) “ell”
- B) “H”
- C) “ello”
- D) “ell” (A)
18-How can you split a string into an array of words?
- A) split(” “)
- B) split(“”)
- C) split()
- D) split(“,”) (A)
19-Which method returns a new string with whitespace removed from both ends?
- A) trim()
- B) removeWhitespace()
- C) clean()
- D) strip() (A)
20-What is the output of the following code: console.log(“Hello”[2]);?
- A) “e”
- B) “l”
- C) “o”
- D) “llo” (B)
21-How can you check if a string contains a specific substring?
- A) includes()
- B) contains()
- C) hasSubstring()
- D) checkSubstring() (A)
22-What is the output of the following code: console.log(“Hello”.toUpperCase().charAt(1));?
- A) “e”
- B) “L”
- C) “l”
- D) “E” (D)
23-Which method is used to split a string at each occurrence of a specified character?
- A) split()
- B) divide()
- C) explode()
- D) separate() (A)
24-What does the length property return for a string?
- A) The number of characters in the string
- B) The index of the last character in the string
- C) The first character of the string
- D) The ASCII value of the last character in the string (A)
25-How can you extract a substring from the start to the end of a string?
- A) str.substring(0)
- B) str.substring(0, str.length)
- C) str.substring(1)
- D) str.substring(str.length – 1) (B)
Reference
Here are some references you can use to learn more about JavaScript strings:
JavaScript Strings – W3Schools:
Book: “Eloquent JavaScript” by Marijn Haverbeke (Chapter 4)
JavaScript String Methods – GeeksforGeeks:
