Healthy and unhealthy food
The Battle of the Bites: Unveiling the Secrets of Healthy and Unhealthy Foods
Introduction
In a world of fast-paced lives and hectic schedules, our food choices often become a reflection of our lifestyle.
The age-old debate of healthy versus unhealthy foods continues to influence our dietary decisions.
With an ever-growing awareness of the impact of diet on our overall well-being, it’s crucial to understand the distinctions between these two categories and make informed choices.
article will explore the characteristics of both healthy and unhealthy foods, shedding light on their effects on our health.
The Good: Healthy Foods
Healthy foods are those that nourish our bodies, providing essential nutrients and contributing to overall well-being. They are typically rich in vitamins, minerals, fiber, and other beneficial compounds. Here are some characteristics of healthy foods:

Nutrient Density: Healthy foods are packed with essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and nuts are excellent examples of nutrient-dense foods.
Low in Empty Calories: These foods are generally low in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and excess calories. They do not contribute to weight gain or health problems when consumed in moderation.
Whole and Unprocessed: Healthy foods are often minimally processed. They are close to their natural state, preserving their nutritional value. Whole grains, fresh produce, and lean proteins are prime examples.
High in Fiber: Fiber is essential for digestive health, weight management, and heart health. Many healthy foods, like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, are excellent sources of fiber.
Variety: A balanced diet consists of a variety of healthy foods.
This diversity ensures that your body receives all the necessary nutrients.
Positive Impact on Health: Regular consumption of healthy foods can lower the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
Example of healthy food
One excellent example of a healthy food is a colorful and nutrient-rich salad. Let’s break down the elements that make a salad a healthy choice:
Fresh Vegetables: A healthy salad starts with a base of fresh, leafy greens like spinach, kale, or mixed greens. These greens are rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber, promoting good digestion and overall health.
Vibrant Colors: A variety of colorful vegetables, such as tomatoes, bell peppers, carrots, and red onions, are often added to salads. These colors indicate a diverse range of nutrients, including vitamin C, vitamin A, and antioxidants.
Protein: To make the salad more satisfying and balanced, lean sources of protein like grilled chicken, tofu, beans, or quinoa can be added. Protein supports muscle health, energy, and helps control hunger.
Healthy Fats: Incorporating healthy fats, such as avocado slices or a sprinkle of nuts or seeds, enhances the taste and provides essential fatty acids that are beneficial for the heart and brain.
Dressing: Opting for a vinaigrette made with olive oil and balsamic vinegar, or a yogurt-based dressing, instead of heavy, calorie-laden dressings, keeps the salad nutritious and delicious. Healthy fats like those found in olive oil can improve nutrient absorption.
Fiber: All the vegetables and ingredients in a salad are high in fiber, which aids in digestion and helps you feel full, reducing overeating.
Low Caloric Density: Salads are often low in calories while being filling due to their high water content and fiber. This makes them an excellent choice for weight management.
Versatility: Salads are incredibly versatile and can be tailored to suit individual tastes and dietary preferences. You can add fruits like berries, apples, or oranges for a touch of sweetness or sprinkle some cheese for added flavor.
Hydration: The water content in vegetables and the moisture from a light dressing contribute to hydration, an important aspect of overall health.
Nutrient Density: Salads offer a high level of nutrient density, which means you get a significant amount of essential nutrients with relatively few calories.
Eating a colorful and nutrient-rich salad as part of your regular diet is a great way to ensure you’re getting a wide range of essential nutrients, promoting good health, and maintaining a balanced diet. Plus, the combination of flavors and textures in a well-made salad can be truly satisfying, making it an enjoyable and healthy food choice.
The Bad: Unhealthy Foods
Unhealthy foods are often loaded with empty calories, artificial additives, and unhealthy fats, posing a range of risks to our health.
Here are some characteristics of unhealthy foods:
High in Added Sugars: Sugary foods and beverages are major culprits when it comes to unhealthy eating. Excessive sugar consumption is linked to obesity, type 2 diabetes, and dental problems.
Trans Fats and Saturated Fats: Many unhealthy foods contain trans fats and saturated fats, which can raise LDL cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease.
Processed and Ultra-Processed: Unhealthy foods are often heavily processed, containing artificial flavors, preservatives, and unhealthy additives. Fast food, sugary snacks, and many convenience foods fall into this category.
Empty Calories: These foods provide little to no nutritional value. They offer little more than a quick burst of energy, followed by a crash.
High in Sodium: Processed and fast foods are often high in salt, contributing to hypertension and cardiovascular issues.
Negative Impact on Health: A diet rich in unhealthy foods is associated with obesity, heart disease, high blood pressure, and other health problems.
Example of unhealthy food
An example of unhealthy food is a double cheeseburger meal from a fast-food restaurant. Let’s examine the characteristics that make this a less healthy food choice:
High in Saturated Fat: A double cheeseburger is typically made with two beef patties, and these are often high in saturated fat, which can raise LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease.

Excess Calories: The large size of the burger and accompanying meal (fries and a soda) can result in an excessive calorie intake in a single meal. Consuming more calories than your body needs can lead to weight gain and obesity.
Processed Ingredients: Fast-food burgers often contain processed ingredients, including additives, preservatives, and artificial flavors, which can be detrimental to overall health.
Trans Fats: Many fast-food establishments use trans fats in their cooking oils, which are known to be harmful and can increase the risk of heart disease.

High Sodium Content: The burger and fries are often heavily salted, contributing to high sodium intake, which can lead to hypertension and other cardiovascular problems.
Lack of Fiber: Fast food items like double cheeseburgers typically lack dietary fiber, which is essential for good digestion and can help you feel full for longer.
Empty Calories: While the meal provides a quick burst of energy due to the high carbohydrate content, it lacks the essential nutrients found in healthier options.
Low Nutrient Density: Fast food items like double cheeseburgers do not offer a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients. They are often referred to as “junk food” because of this.
Overconsumption of Sugar: Sugary sodas are often included in these meals, contributing to excessive sugar consumption, which is linked to obesity and various health issues.
Convenience Over Nutrition: Fast food is known for its convenience, but it often prioritizes speed and taste over nutritional value.
While indulging in fast food occasionally is not inherently harmful, regular consumption of meals like double cheeseburgers can have negative long-term health consequences, including obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. It’s important to be mindful of such choices and aim for a balanced diet that includes a variety of healthier foods to support your overall well-being.
Harms of unhealthy food
Unhealthy foods, also known as junk or processed foods, can have a range of negative effects on your health and well-being. Consuming these foods regularly can lead to various health issues. Here are some of the harms of unhealthy food:
Weight Gain and Obesity: Unhealthy foods are often calorie-dense, high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and low in essential nutrients. Consuming them can lead to excess calorie intake, which in turn contributes to weight gain and obesity.
Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases: Regular consumption of unhealthy foods is associated with an increased risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, certain types of cancer, and metabolic syndrome.
Poor Nutrient Intake: Unhealthy foods are typically low in essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Relying on these foods can result in nutrient deficiencies and overall poor health.
Digestive Issues: High-fat, low-fiber diets that are common with unhealthy foods can lead to digestive problems, including constipation and indigestion.
High Blood Pressure: Processed foods often contain high levels of salt (sodium), which can lead to high blood pressure (hypertension), increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
High Cholesterol: Trans fats and saturated fats in unhealthy foods can raise LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease.
Insulin Resistance: The high sugar content of unhealthy foods can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes.
Dental Issues: Sugary and acidic foods and beverages can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease.
Negative Impact on Mental Health: Diets high in unhealthy foods have been linked to an increased risk of depression and other mental health issues.
Energy Fluctuations: Unhealthy foods can cause rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels, leading to low energy levels and irritability.
Increased Inflammation: Many unhealthy foods promote inflammation in the body, which is linked to various chronic diseases and conditions.
Harmful Food Additives: Unhealthy foods often contain artificial additives, preservatives, and flavor enhancers, which can have negative health effects.
Shortened Lifespan: A diet primarily composed of unhealthy foods can lead to a shorter lifespan and a lower quality of life in later years.
Addictive Properties: Certain unhealthy foods, particularly those high in sugar and salt, can have addictive qualities, making it challenging to break away from unhealthy eating habits.
Impaired Cognitive Function: Unhealthy eating can negatively impact cognitive function, including memory and focus.
Harm to the Environment: The production and consumption of unhealthy foods, such as fast food, can contribute to environmental issues like deforestation and excessive greenhouse gas emissions.
It’s important to limit the consumption of unhealthy foods and focus on a balanced diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods to promote optimal health and well-being. Making informed and mindful food choices is crucial for long-term health.
Beneficial of healthy food
Healthy food offers a wide range of advantages for both your physical and mental well-being. Here are some of the key benefits of consuming a diet rich in healthy foods:
Nutrient-Rich: Healthy foods are packed with essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which are vital for overall health and well-being.
Weight Management: Healthy foods are typically lower in calories, saturated fats, and added sugars, making them a crucial component of weight management and maintaining a healthy body weight.
Disease Prevention: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can reduce the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Improved Digestion: High-fiber foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains support healthy digestion and help prevent digestive issues like constipation.
Heart Health: Healthy foods, particularly those low in saturated fats, can lower the risk of heart disease by reducing cholesterol levels and maintaining healthy blood pressure.
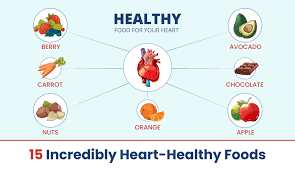
Energy and Vitality: Nutrient-dense foods provide sustained energy throughout the day, preventing energy spikes and crashes associated with high-sugar, low-nutrient diets.
Mental Well-Being: A diet rich in healthy foods is associated with better mental health. Nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish, can support brain health and reduce the risk of depression and cognitive decline.
Strong Bones and Teeth: Foods high in calcium and vitamin D, such as dairy products and leafy greens, support bone health and help prevent conditions like osteoporosis.
Clearer Skin: Nutrient-rich foods can promote clear, healthy skin by providing the vitamins and minerals necessary for a radiant complexion.
Longevity: Consuming a diet rich in healthy foods is linked to a longer life and increased longevity.
Improved Immune System: Nutrient-dense foods, particularly those high in vitamins C and E, can strengthen the immune system, helping the body fight off illnesses and infections.
Enhanced Cognitive Function: A diet high in antioxidants, found in fruits and vegetables, can help protect brain cells and maintain cognitive function as you age.
Sustainable Energy: Healthy foods provide a steady source of energy, allowing you to stay alert and productive throughout the day.
Reduced Inflammation: A diet rich in healthy foods can reduce inflammation in the body, which is associated with various chronic diseases.
Better Sleep: Nutrient-dense foods can improve sleep quality and help regulate your sleep patterns.
Improved Mood: Healthy eating is associated with a more positive and stable mood, reducing the risk of mood disorders and promoting overall well-being.
Environmental Impact: Many healthy food choices, such as plant-based diets, have a lower environmental impact and contribute to sustainability.
Incorporating a variety of healthy foods into your diet and maintaining a balanced eating pattern is essential for reaping these numerous advantages. A well-rounded diet that focuses on whole, unprocessed foods is key to promoting a healthy and vibrant life.
Conclusion
In the battle between healthy and unhealthy foods, the outcome is clear: choosing nutrient-dense, unprocessed options is the key to better health and well-being. It’s essential to recognize that occasional indulgences in unhealthy foods are not inherently harmful, but they should be enjoyed in moderation.
By incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and nuts into your diet, you can ensure that your body receives the necessary nutrients to function at its best. While it may be challenging to break free from unhealthy food habits, the long-term benefits of a nutritious diet are well worth the effort.
Ultimately, a balanced diet and a thoughtful approach to food choices are the cornerstones of a healthy lifestyle. Educating ourselves about the differences between healthy and unhealthy foods is the first step towards achieving a happier, healthier life.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): https://www.cdc.gov/
National Institutes of Health (NIH): https://www.nih.gov/
World Health Organization (WHO): https://www.who.int/
ChooseMyPlate.gov: https://www.choosemyplate.gov/ (U.S. Department of Agriculture)
Books:
“The China Study” by T. Colin Campbell and Thomas M. Campbell II
“In Defense of Food” by Michael Pollan
“The Blue Zones Solution” by Dan Buettner
“Eating on the Wild Side” by Jo Robinson
“The Omnivore’s Dilemma” by Michael Pollan




